Text Processing (Pipelines)¶
Text processing (Pipelines) is used for data parsing. By defining parsing rules, various data types are cut into structured data that meet our requirements. For example, the timestamp of the log, the status of the log, and other specific fields are extracted by Pipeline as labels.
Preconditions¶
- Install DataKit
- DataKit version requires to be equal to or higher than 1.5.0.
To ensure the proper use of Pipeline, upgrade DataKit to 1.5.0 and above. A lower version will lead to some Pipeline functions failure. Before DataKit<1.5.0 version:
-
Default Pipeline is not supported;
-
Multiple selection of data sources is not supported, and only one source can be selected per Pipeline. Therefore, if your version is lower than 1.5.0 and you choose multiple data sources, it will not take effect;
-
Pipeline name for fixed build does not support modifications. For example, if the log source is nginx, the pipeline name is fixed to nginx.p. Therefore, if your version is lower than 1.5.0 and the Pipeline name is inconsistent with the data source name, the Pipeline will not take effect;
Create Pipeline¶
In the Guance workspace Management > Pipelines, click Create to create a new pipeline file. Or you can click Pipelines to create it in the shortcut entry of metrics, logs, user access, application performance, infrastructure and security check function directory.
Note: After the pipeline file is created, DataKit needs to be installed before it will take effect. DataKit will get the configured pipeline file from the workspace regularly. The default time is 1 minute, which can be modified in conf.d/datakit.conf.
Configuration Description¶
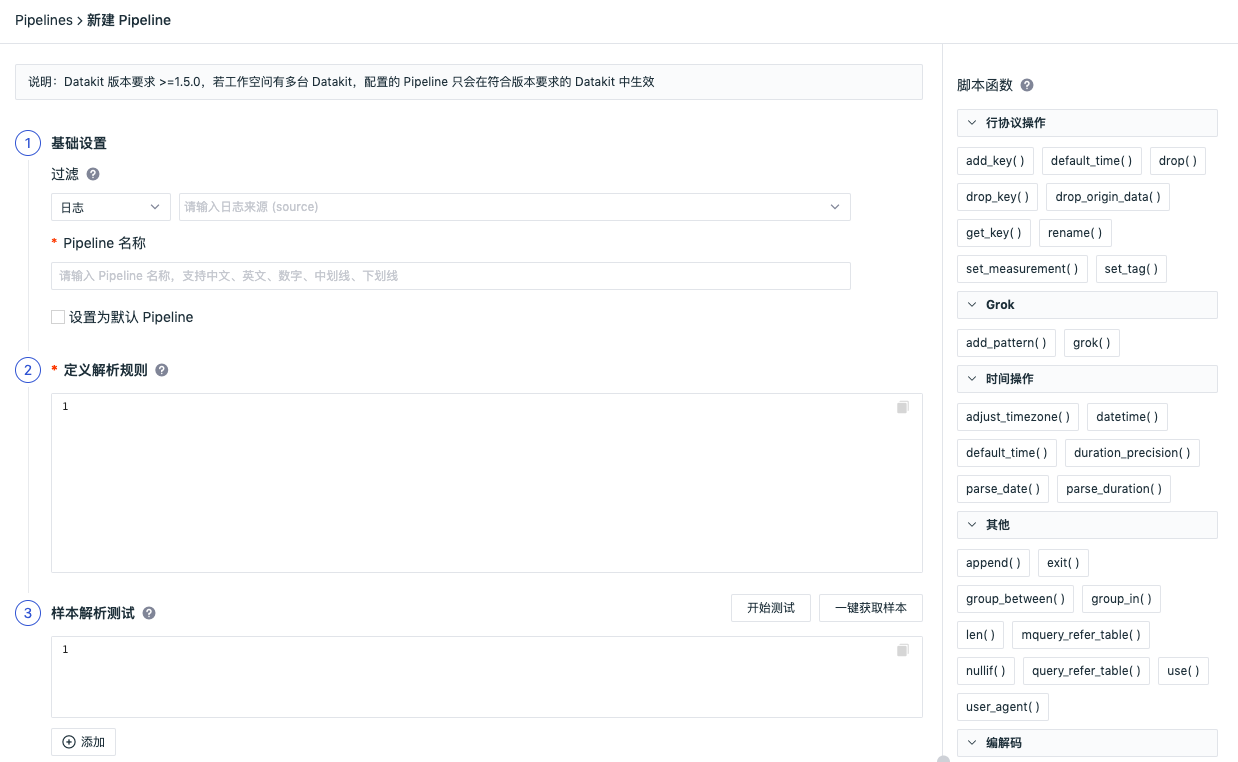
On the new pipeline page, you can first Filter out the data range you want to process text, and then Define Parsing Rules. If you want to test whether the input parsing rules are correct and effective, you can enter the corresponding data in Sample Parsing Test for testing. After passing the test, click Save to create a pipeline file.
1. Basic Settings
- Filtering: data types include logs, metrics, RUM, APM, basic objects, custom objects, networks, security check and multiple choices are supported;
- Pipeline name: Enter a custom Pipeline file name;
Warning
The custom Pipeline file cannot have the same name, but its name can be the same with the official Pipeline's. In this case, DataKit will automatically obtain the custom Pipeline file configuration first. If you manually configure the Pipeline file name in the .conf file of the collector, DataKit takes precedence over the manually configured Pipeline file name.
- Set as default Pipeline: Check Set as default Pipeline. If the current data type does not match other Pipeline scripts when matching Pipeline processing, the data will be processed according to the rules of the default Pipeline script.
Warning
Only one Default Pipeline can be set for each data type. A confirmation box will pop up when there is duplication when creating/importing, asking whether to replace it. It has been checked as the default Pipeline, and there will be a Default mark after the name.
2. Define Parsing Rules
Define parsing rules for data from different sources support a variety of script functions, and the syntax format can be viewed directly through the script function list provided by Guance, such as add_pattern(); See Pipeline manual for more information;
3. Sample Analysis Test
According to the selected data type, input the corresponding data, and test it based on the configured parsing rules.
- Click One-click Collection of Samples to automatically obtain the collected data;
- Click Add to add multiple sample data (up to 3 pieces);
- Click Start Test to return multiple test results; If you enter more than one sample data in the same test text box for testing, only one test result will be returned.
Warning
Pipeline created in Guance workspace is stored in the <datakit installation directory>/Pipeline_remote directory, and each type of Pipeline file is stored in the corresponding secondary directory, where the files in the primary directory are log Pipeline by default. If the metric cpu.p is stored in the <datakit installation directory >/Pipeline_remote/metric/cpu.p directory, refer to the doc Pipeline Category Data Processing.
Test Pipeline¶
On the Pipeline editing page, you can test the filled-in parsing rules by entering data in the Sample Parsing Test. If the parsing rules do not conform, you will return the error prompt result. Sample analysis test is not required. After sample analysis test, the test data is saved synchronously.
One Click to Get Sample Test¶
Guance supports one-click collection of sample test data. When creating or editing Pipeline, click One-click Collection of Samples under Sample Analysis Test, and the system will automatically select the latest data from the collected data reported to the workspace according to the screened data range, and fill it into the test sample box as a sample for testing. When obtaining sample data with one click, only the data in the last 6 hours will be queried each time. If no data is reported in the last 6 hours, it cannot be obtained automatically.
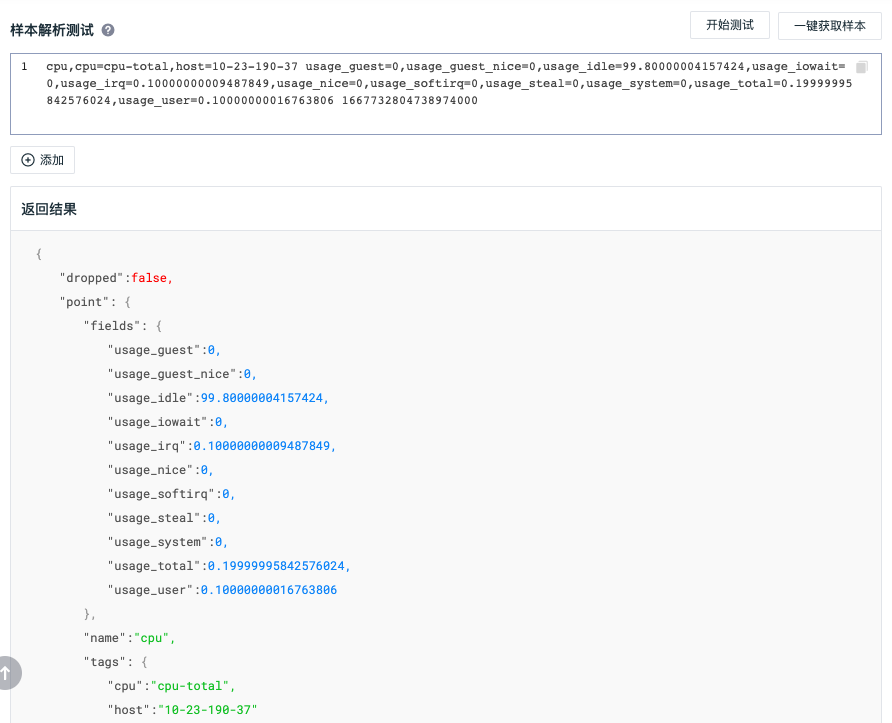
Testing sample:
The following is a sample of reported metric data obtained with one click. The measurement is cpu, and the labels are cpu and host. The fields from usage_guest to usage_user are metric data, and the last 1667732804738974000 is the timestamp. From the return results, we can clearly understand the data structure of one-click sample.
Manually Enter Sample Test¶
You can also enter sample data directly and manually for testing. Guance supports two format types:
- Log data can be directly input into message content for testing in sample parsing test. For more log Pipeline, please refer to the doc Log Pipeline User Manual;
- Other data types first convert the content into line protocol format, and then input it for sample analysis test.
Line Protocol Sample¶
Example description:
- Cpu and redis are index sets; tag1 and tag2 are tag sets; f1, f2, and f3 are field sets (where f1=1i is int, f2=1. 2 is float by default, and f3= "abc" is string); 162072387000000000 is the timestamp;
- The measurement and the tag set are separated by commas; A plurality of labels are separated by commas;
- A space separates the tag set from the field set; Multiple fields are separated by commas;
- A space separates the field set from the timestamp; Timestamp required;
- If it is object data, it must have a
namelabel, otherwise the protocol will report an error; It is best to have amessagefield, which is mainly convenient for full-text search.
See DataKit API for more line protocol details.
For more information on how to get the line protocol data, configure the output file of output_file in conf.d/datakit.conf and view the line protocol in that file.
Terminal Command Line Testing¶
In addition to testing Pipeline from Guance studio, you can also test Pipeline from the terminal command line. See How to Write Pipeline Script for more information.
Configuration Sample¶
Examples of Pipeline configuration can be found in the doc Log Pipeline Use Manual and DataKit Pipeline Use Manual.
Related Operations¶
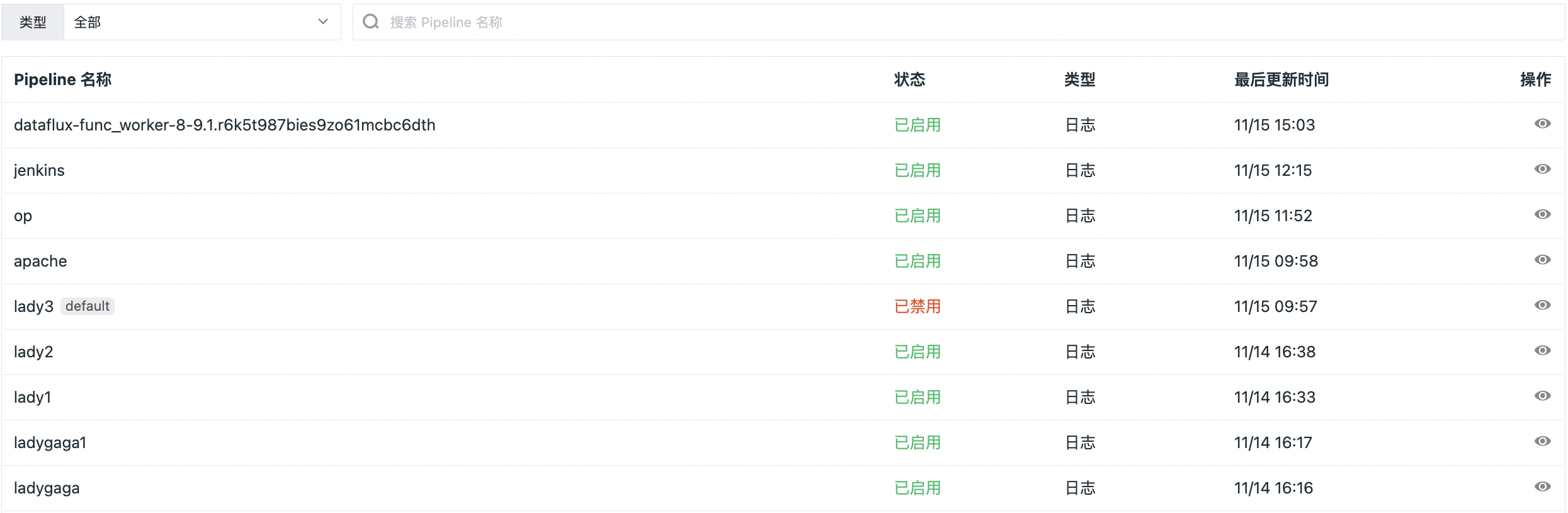
Edit/Delete/Enable/Disable Pipeline¶
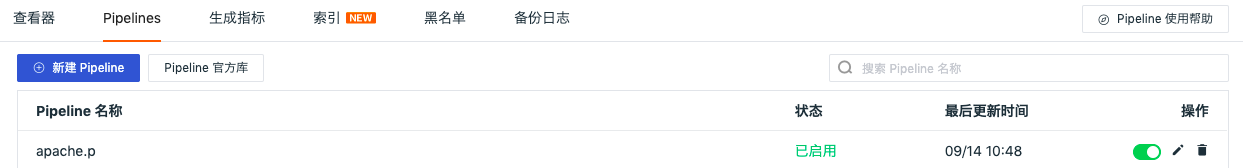
In Guance workspace Management > Pipelines, click the button under the operation on the right to edit/delete/enable/disable the pipeline file.
Note:
- After editing the pipeline file, the default effective time is 1 minute;
- After deleting the pipeline file, it cannot be restored and needs to be recreated; If there is an official library pipeline file with the same name, DataKit will automatically match the official library pipeline file for text processing;
- After the pipeline file is disabled, it can be restored by enabling; If there is an official library pipeline file with the same name, DataKit will automatically match the official library pipeline file for text processing;
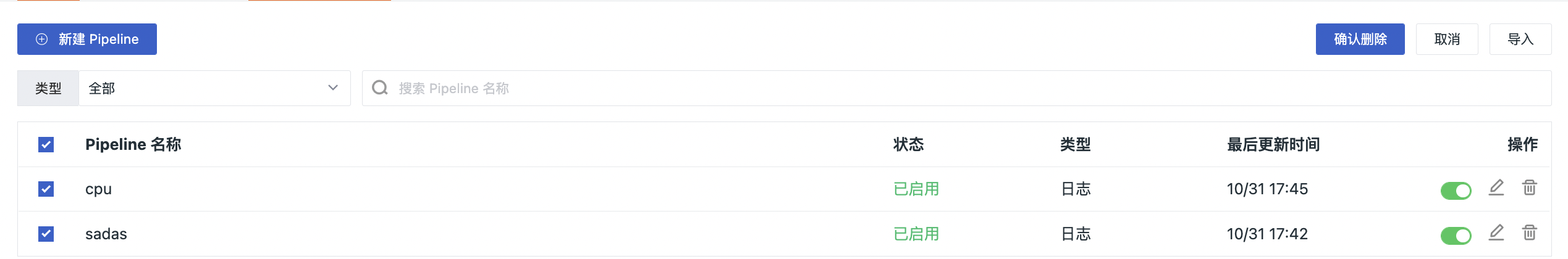
Batch¶
Batch function supports users to Batch Export and Batch Delete in the pipeline file list. By selecting batch operations, you can select multiple pipeline files for export and deletion at the same time.
In Guance workspace Management > Text Processing, click Batch to Batch Export or Batch Delete Pipelines.
Warning
This function is only displayed for workspace owners, administrators and standard members, but not for read-only members.
Import/export¶
You can Import/export Pipeline in Guance workspace Management > Text Processing (Pipelines), that is, create Pipeline by importing/exporting JSON files.
Warning
The imported JSON file needs to be the configuration JSON file from Guance.
Select the pipeline file to be deleted, and click Confirm to delete the current pipeline file.
Pipeline Official Library¶
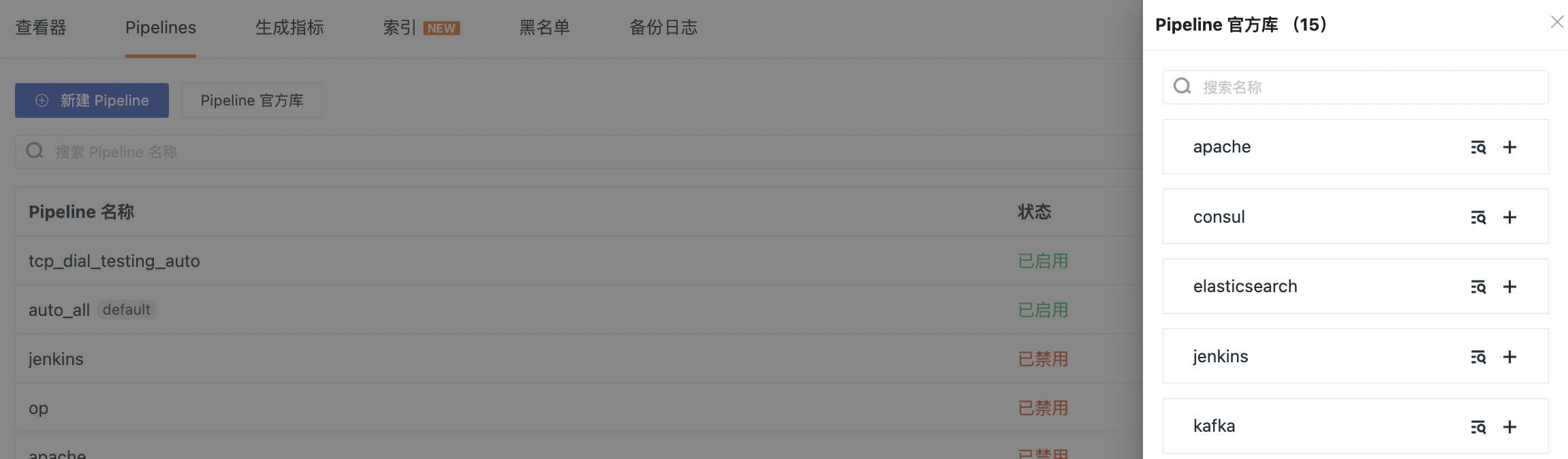
Guance provides a standard official Pipeline library for log data to help you quickly structure your log data.
In Guance workspace Log > Pipeline, click Pipeline Official Library to view the built-in standard pipeline official website file library, including nginx, apache, redis, elasticsearch, mysql and so on.
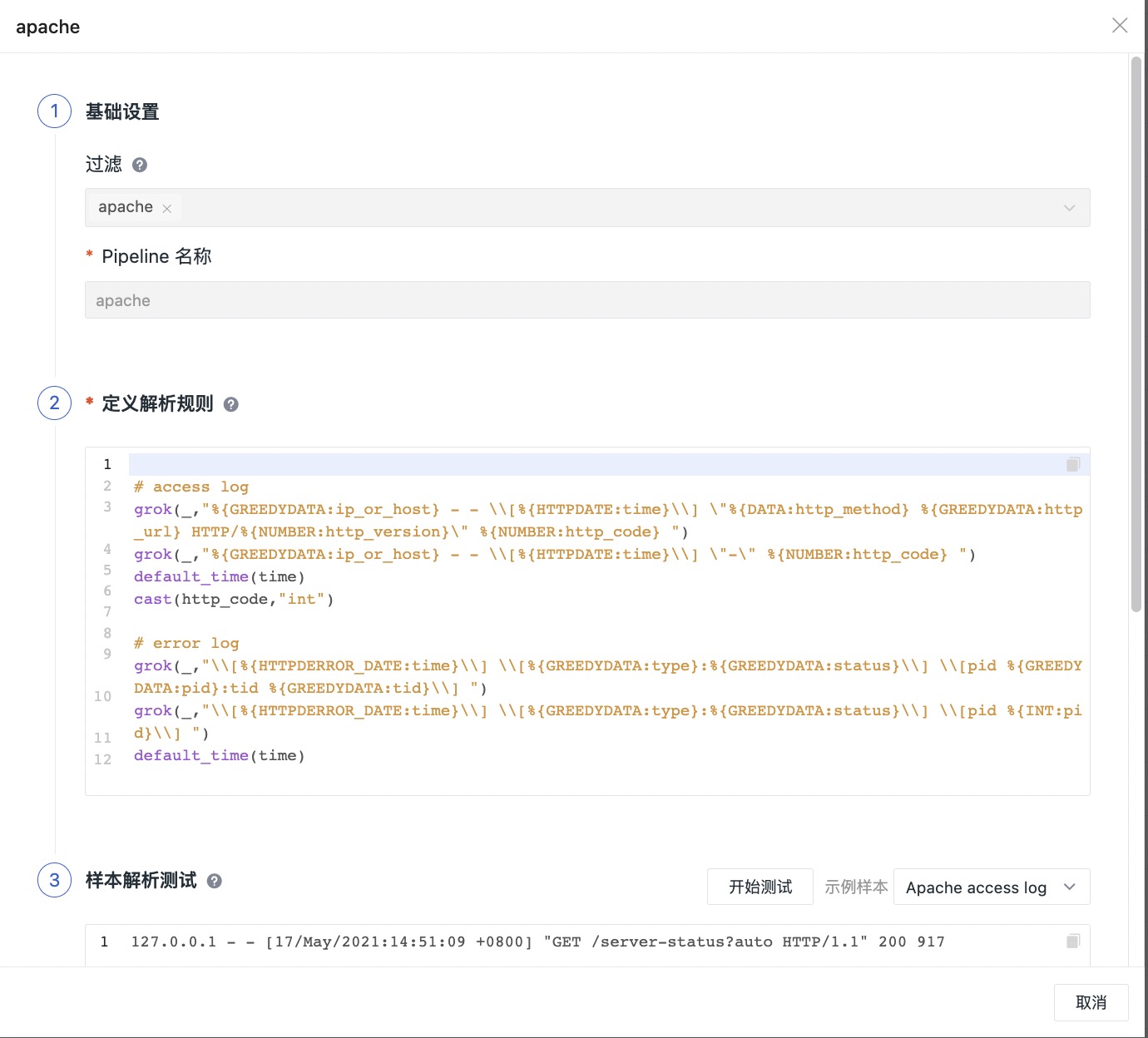
Select to open any pipeline file, such as apache.p, and you can see the built-in parsing rules. If you need to customize and modify it, you can click Clone in the upper right corner.
Note:
- The official pipeline library file does not support modifications.
- Pipeline official library comes with multiple log sample test data, and you can select the log sample test data that meets your own needs before Clone.
- After the cloned Pipeline is modified and saved, the log sample test data is saved synchronously.
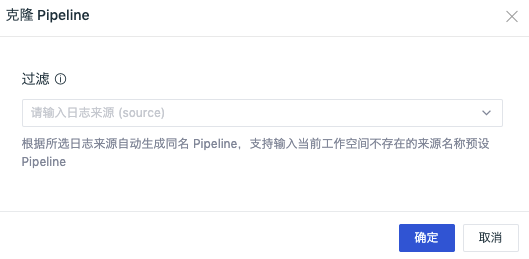
Automatically generate the pipeline file name with the same name according to the selected log source, and click Confirm to create a custom pipeline file.
Warning
DataKit will automatically obtain the official library pipeline file. If the cloned custom pipeline file has the same name as the official pipeline, DataKit will give priority to automatically obtaining the newly built custom pipeline file configuration; If the cloned custom pipeline file has a different name from the official pipeline, the file name of the corresponding pipeline needs to be modified in the pipeline of the corresponding collector.
After the creation is completed, you can view all the custom pipeline files that have been created in Log > Pipeline.
Notes:¶
Pipeline can do the following operations on the data collected by DataKit:
-
Add, delete, modify values or data types for field and tag
-
Change field to tag
-
Modify the measurement name
-
Drop current data
drop()) -
Terminate the run of the Pipeline script(
exit())
When using Pipeline to process different data types, it will affect the original data structure. It is recommended to confirm that the data processing results meet expectations through debugging before using it.