Cross-Workspace Index Query¶
Note
To centrally manage, search, and analyze various logs, Guance can collect logs to unify log data reporting into the Guance workspace. Logs within the workspace can be viewed and searched using the log Explorer, enabling more comprehensive log data analysis.
Additionally, the Guance platform provides index functionality. This defines classification rules for log data, allowing users to save and access logs through different indexes and apply storage policies as needed to effectively control storage costs.
Why Is Cross-Workspace Index Query Needed?¶
Feature Characteristics:
From the previous sections, it is not difficult to understand the characteristics of logs and indexes: both logs and indexes are associated with the respective workspace. Logs are stored within a workspace, and indexes are special classification and storage rules created for log data within that space.
Business Challenges:
To meet requirements such as cost accounting for each team or controlling data resource permissions, enterprises often create multiple workspaces on Guance for data management. While this model enables departmental data management, it is not conducive to global data analysis.
Necessity of Cross-Workspace Index Query:
To perform global data analysis under a distributed data management model, Guance provides cross-workspace query functionality, which allows accessing log data from other workspaces.
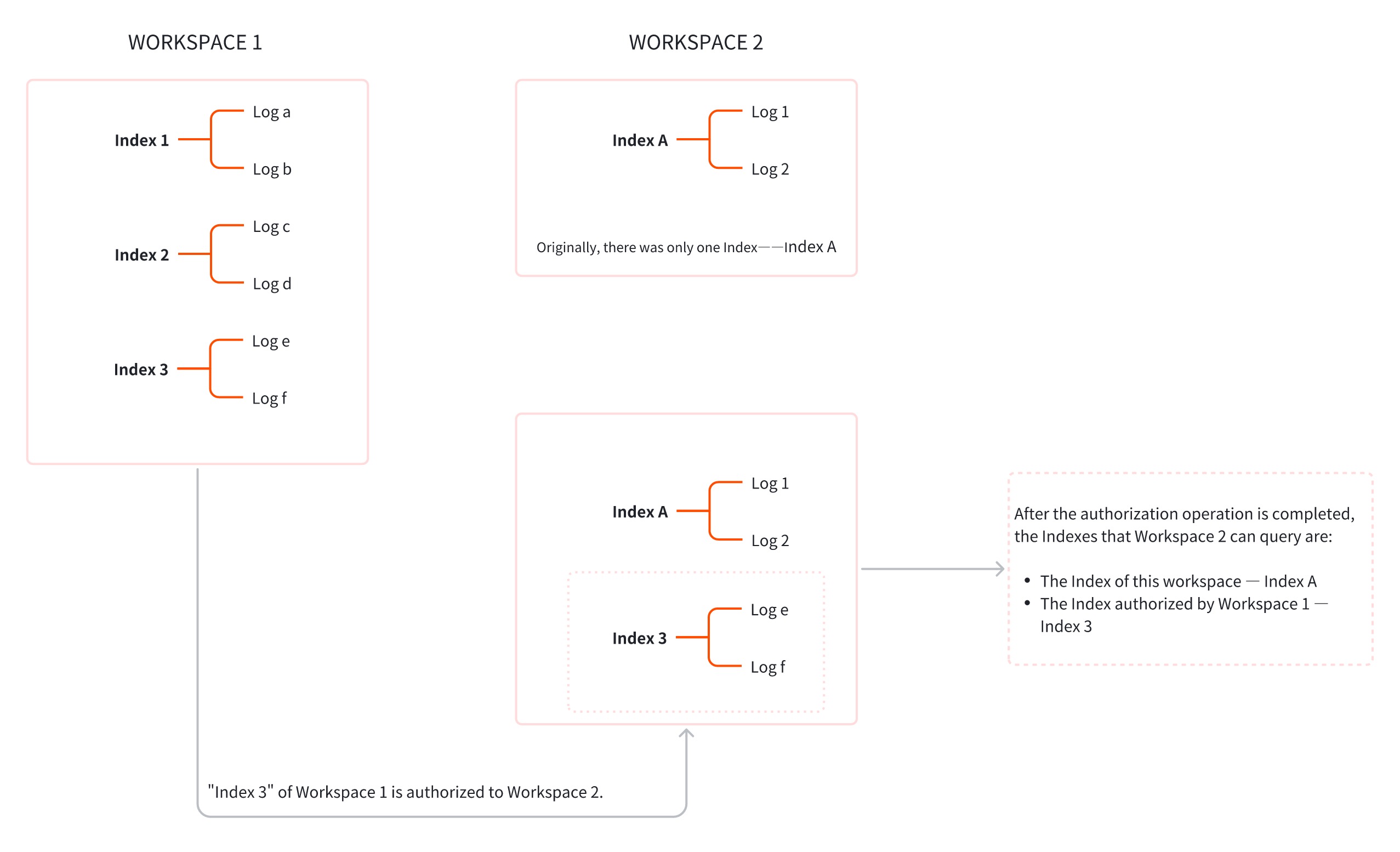
Specifically, since logs are classified by indexes, granting index data from "Workspace 1" to "Workspace 2" enables viewing "Workspace 1"’s indexes in "Workspace 2"’s log Explorer, thus accessing corresponding indexed log data.
This feature overcomes the limitations of log data storage locations, significantly improving the efficiency of data analysis and fault location.
Getting Started¶
Scenario Example: If index data from "Workspace 1" is granted to "Workspace 2", then for "Workspace 2", two types of indexes can be accessed:
Querying Original Indexes in This Workspace¶
Enter the log Explorer of "Workspace 2". The "Workspace" bar in the top-left corner defaults to the current workspace.
The quick filter on the left lists all available original indexes in this workspace, including: default index, log index, and external index.
Note: External indexes are single-select.
Querying Indexes Authorized from Other Workspaces¶
To have "Workspace 2" call index data from "Workspace 1", follow these two steps for cross-workspace index authorization:
- In the workspace requiring authorization (Workspace 1), authorize the corresponding log items and indexes;
- Enter the authorized workspace (Workspace 2) to select and apply the index items.
For detailed operation instructions, refer to Cross-Workspace Authorization.
After completing these two steps, "Workspace 1" has granted index authorization to "Workspace 2". Now enter the authorized workspace---"Workspace 2" > Log Explorer.
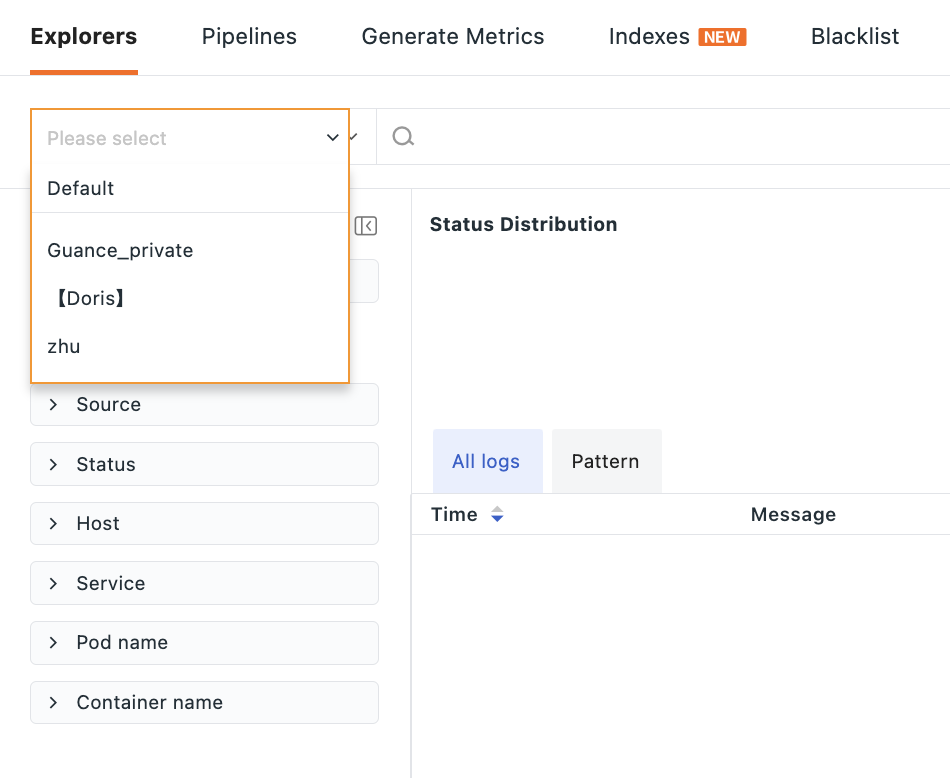
Selecting a Workspace¶
Click the Workspace dropdown box to view all selectable workspaces. Single or multiple selections are supported.
Note
- The list of selectable workspaces only includes those meeting three conditions: belonging to the same cluster; having completed authorization operations; and the authorized data scope including log data.
- Selecting a single workspace will display its name directly in the workspace bar; selecting multiple workspaces will show "n items selected," and clicking will reveal specific options.
Selecting an Index¶
After selecting a workspace, the indexes under that workspace will be listed in the Quick Filter section:
Note
- External indexes do not support cross-workspace queries. They can only be used when selecting the current workspace. If another workspace is selected, external indexes will be unavailable.
- Log indexes default to
default. When selecting multiple workspaces, all default indexes from multiple spaces will be grouped under the samedefaultindex. - Only authorized indexes within the authorized scope will be listed for cross-workspace authorization.
Analyzing Log Data¶
Note: Cross-workspace index queries only affect the channels through which log data is obtained, while other log analysis functions remain unaffected.
After selecting the workspace and indexes in the log Explorer, you can use the existing features of the log Explorer normally, such as search, quick filtering, status chart display, and analysis.
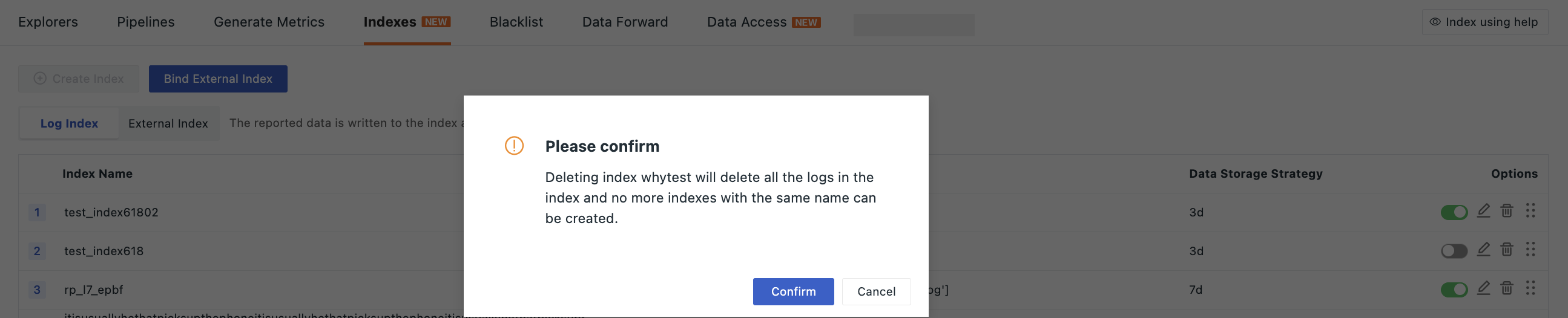
Deleting an Index¶
If deleting an index whytest from Workspace 1, since this index has been authorized to other spaces, a confirmation prompt will appear when deleting. Click Confirm to delete the index.
Once confirmed, this change will immediately impact "Workspace 2," making the corresponding index unavailable.