OTEL SQL Sanitization¶
Author: Song Longqi
SQL sanitization is also narrowly defined as DB statement cleaning.
According to the official OTEL statement:
The agent cleans all database queries/statements before setting the `db.statement` semantic attribute. All values (strings, numbers) in the query string are replaced with a question mark (?), and the entire SQL statement is formatted (replacing newline characters with spaces, leaving only one space) among other operations.
Example:
- SQL query SELECT a from b where password="secret" will appear in the span as SELECT a from b where password=?
By default, this behavior is enabled for all database detections. Use the following attributes to disable it:
System property: otel.instrumentation.common.db-statement-sanitizer.enabled
Environment variable: OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_COMMON_DB_STATEMENT_SANITIZER_ENABLED
Default value: true
Explanation: Enables DB statement cleaning.
DB Statement Cleaning and Results¶
Most statements include some sensitive data such as usernames, phone numbers, passwords, card numbers, etc. Sensitive data processing can filter out these pieces of information. Another reason is that it facilitates grouping and filtering operations.
There are two ways to write SQL statements:
For example:
ps = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT name,password,id FROM student where name=? and password=?");
ps.setString(1, username); // set replaces the first ?
ps.setString(2, pw); // replaces the second ?
This is the JDBC writing method, which is database-agnostic (both Oracle and MySQL are written this way).
The result is that the chain captures two '?' in db.statement.
A less common alternative writing method:
ps = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT name,password,id FROM student where name='guance' and password='123456'");
// ps.setString(1,username); no longer using set
// ps.setString(2,pw);
In this case, the agent captures the SQL statement without placeholders.
The purpose of OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_COMMON_DB_STATEMENT_SANITIZER_ENABLED is explained here.
The reason is that the agent's probe is on the function prepareStatement or Statement.
To fundamentally solve the sanitization issue, probes need to be added on set. Parameters should be cached before execute(), and ultimately, the parameters should be placed into Attributes.
Guance Secondary Development¶
To obtain the data before cleaning and the values subsequently added via the set function, new instrumentation needs to be performed, along with adding environment variables:
Ultimately, the trace details in Guance will look like this:
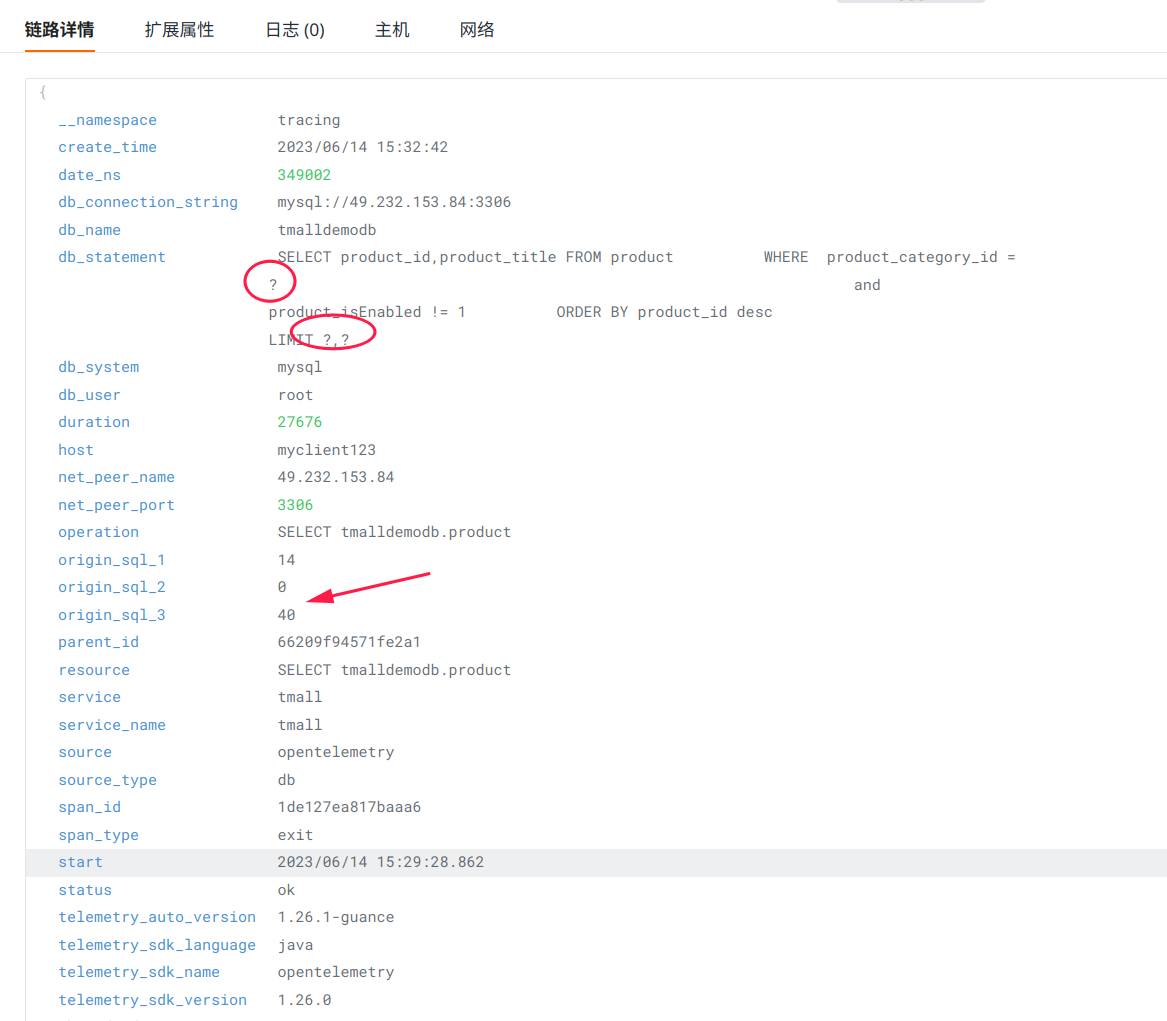
Common Issues¶
-
Enabling
-Dotel.jdbc.sql.obfuscation=truebut not disabling DB statement cleaning -
Enabling
-Dotel.jdbc.sql.obfuscation=trueand disabling DB statement cleaning
If the statement is too long or has many newline characters, and no formatting is applied, the statement will be messy. It will also cause unnecessary traffic waste.
More¶
For other questions, please visit: GitHub-Issue