Customize Dialtesting
In some cases, you may not be able to connect to SAAS's dialing task service. In this case, we can define the dialing task through the local JSON file.
Configuration¶
Configure Collector¶
Go to the conf.d/network directory under the DataKit installation directory, copy dialtesting.conf.sample and name it dialtesting.conf. Examples are as follows:
[[inputs.dialtesting]]
server = "file://</path/to/your/local.json>"
# Note: Taking Linux as an example, assuming your json directory is /some/path/my.json, then the
# server should be written as file:///some/path/my.json
# Note that the following tag suggestions are filled in one by one (do not modify the tag key here), so that the complete dialing test results can be displayed on the page.
[inputs.dialtesting.tags]
country = "<specify-datakit-country>" # Countries where DataKit is deployed
province = "<specify-datakit-province>" # Provices where DataKit is deployed
city = "<specify-datakit-city>" # Cities where DataKit is deployed
isp = "<specify-datakit-ISP>" # Specify the network service provider where DataKit is located
region = "<your-region>" # You can specify a region name at will
The collector can now be turned on by ConfigMap injection collector configuration.
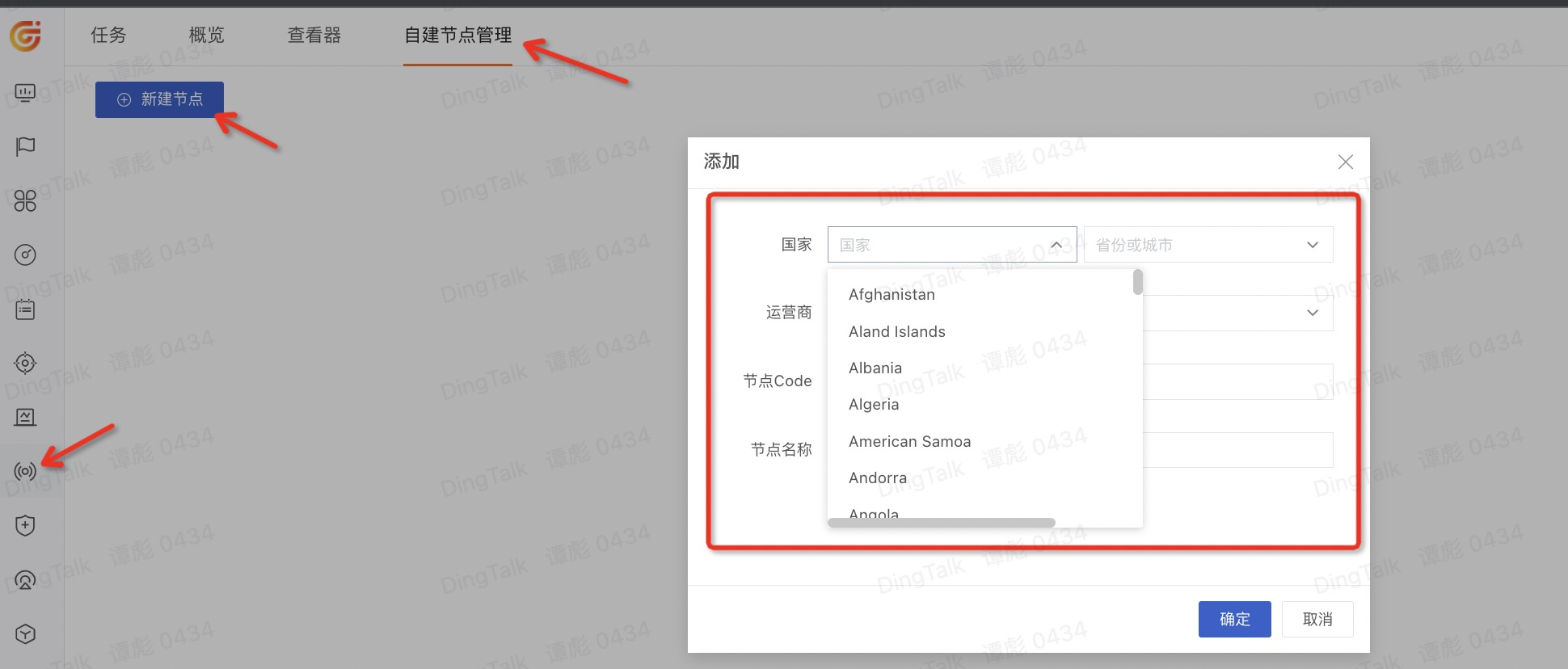
The specific country/region and ISP selection can be selected as shown in the following figure (note that you don't really create a new "self-built node", just provide an alternative source here):
Configure the Dial Test Task¶
At present, the dialing test task supports five dialing test types, namely HTTP, TCP, ICMP, WEBSOCKET and GRPC services. The JSON format is as follows:
The following is a specific dialing test example:
{
"HTTP": [
{
"name": "baidu-json-test",
"method": "GET",
"url": "http://baidu.com",
"post_url": "https://<your-dataway-host>?token=<your-token>",
"status": "OK",
"schedule_type": "frequency",
"frequency": "10s",
"success_when_logic": "and",
"success_when": [
{
"response_time": "1000ms",
"header": {
"Content-Type": [
{
"contains": "html"
}
]
},
"status_code": [
{
"is": "200"
}
]
}
],
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"auth": {}
},
"request_body": {}
},
"update_time": 1645065786362746
}
],
"TCP": [
{
"name": "tcp-test",
"host": "www.baidu.com",
"port": "80",
"status": "OK",
"frequency": "10s",
"success_when_logic": "or",
"success_when": [
{
"response_time": [
{
"is_contain_dns": true,
"target": "10ms"
}
]
}
],
"update_time": 1641440314550918
}
]
}
After editing this JSON, it is recommended to find some(online tools or this tool)to verify that the JSON format is correct. If the JSON format is incorrect, the dialing test will not take effect.
After configuration, restart DataKit.
Test Task Field Definition¶
The dialing task fields include "public fields" and "additional fields" for specific dialing tasks.
Public Field¶
The public fields of dialing test tasks are defined as follows:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
string | Y | Dial test service name |
status |
string | Y | Dial test service status, such as "OK"/"stop" |
frequency |
string | Y | Dial frequency |
schedule_type |
string | Y | The execution type of the monitoring task, such as frequency or crontab, default is frequency |
crontab |
string | N | The crontab expression, such as */10 * * * *, only valid when schedule_type is crontab |
success_when_logic |
string | N | The logical relationship between success_when conditions, such as "and"/"or", defaults to "and" |
success_when |
object | Y | See below for details |
advance_options |
object | N | See below for details |
post_url |
string | N | Send the dialing test result to the workspace pointed by the Token, and if it is not filled in, send it to the workspace where the current DataKit is located |
tags_info |
string | N | Custom tags, such as t1,t2 |
workspace_language |
string | N | Workspace language, such as zh,en |
HTTP Dial Test¶
Extra field:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
method |
string | Y | HTTP request method |
url |
string | Y | Complete HTTP request address |
The overall JSON structure is as follows:
{
"HTTP": [
{
"name": "baidu-json-test",
"method": "GET",
"url": "http://baidu.com",
"post_url": "https://<your-dataway-host>?token=<your-token>",
"status": "OK",
"frequency": "10s",
"success_when_logic": "and",
"success_when": ...,
"advance_options": ...
},
{
... another HTTP dialtesting
}
]
}
success_when Definition¶
The judging conditions used to define the success of dialing test mainly include the following aspects:
- HTTP request returns body judgment(
body)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
is |
string | N | Whether the returned body is equal to the specified field |
is_not |
string | N | Whether the returned body is not equal to the specified field |
match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned body contains a substring of the matching regular expression |
not_match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned body does not contain a substring of the matching regular expression |
contains |
string | N | Whether the returned body contains the specified substring |
not_contains |
string | N | Whether the returned body does not contain the specified substring |
eg.
Here, body can configure multiple verification rules, and the relationship between them is determined by "success_when_logic". When it is configured as and, if any rule is verified, it will be considered that the current dialing test failed; When it is configured to or, if any rule is verified, it will be considered that the current dialing test is successful. The default is an and relationship. The following verification rules all follow this judgment principle.
Note that the regular is escaped correctly here, and the actual regular expression in the example is
\d\d.*.
- HTTP request returns header judgment (
header)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
is |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field is equal to the specified value |
is_not |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field is not equal to the specified value. |
match_regex |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field contains a substring of the matching regular expression. |
not_match_regex |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field does not contain a substring of the matching regular expression. |
contains |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field contains the specified substring. |
not_contains |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field does not contain the specified substring. |
for example:
Because there may be decisions for multiple types of headers, validation for multiple headers can also be configured here:
"success_when": [
{
"header": {
"Content-Type": [
{
"contains": "some-header-value"
}
],
"Etag": [
{
"match_regex": "\\d\\d-.*"
}
]
}
}
]
- HTTP request returns status code (
status_code)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
is |
string | N | Whether the status code returned is equal to the specified field |
is_not |
string | N | Whether the status code returned is not equal to the specified field |
match_regex |
string | N | Whether the status code returned contains a substring of the matching regular expression |
not_match_regex |
string | N | Whether the status code returned does not contain a substring of the matching regular expression |
contains |
string | N | Whether the status code returned contains the specified substring |
not_contains |
string | N | Whether the status code returned does not contain the specified substring |
for example:
For a certain URL dial test, its HTTP return is usually only one, so only one validation rule is generally configured here (although multiple array configurations are supported).
- HTTP request response time (
response_time)
Only one time value can be filled in here. If the response time of the request is less than the specified value, the dialing test is judged to be successful, such as:
Note that the time units specified here are
ns(nanoseconds)/us(microseconds) /ms(milliseconds) /s(seconds) /m(minutes) /h(hours). For HTTP dial testing,msunits are generally used.
Several kinds of judgment basis listed above can be used in combination, and the relationship between them is determined by "success_when_logic". When it is configured as and, if any rule is verified, it is considered that the current dialing test fails; When it is configured to or, if any rule is verified, it will be considered that the current dialing test is successful; The default is an and relationship. Such as:
"success_when": [
{
"response_time": "1000ms",
"header": { HTTP header 相关判定 },
"status_code": [ HTTP 状态码相关判定 ],
"body": [ HTTP body 相关判定 ]
}
]
advance_options Definition¶
Advanced options are mainly used to adjust specific dialing behavior, mainly in the following aspects:
- HTTP Request Option (
request_options)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
follow_redirect |
bool | N | Whether redirect jump is supported |
headers |
map[string]string | N | Specify a set of headers on an HTTP request |
cookies |
string | N | Specify the requested Cookie |
auth |
object | N | Specify the authentication method of the request |
Among them, auth only supports ordinary username and password authentication, which is defined as follows:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
username |
string | Y | User name |
password |
string | Y | User name and password |
request_options example:
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"auth": {
"username": "zhangsan",
"password": "fawaikuangtu"
},
"headers": {
"X-Prison-Breaker": "zhangsan",
"X-Prison-Break-Password": "fawaikuangtu"
},
"follow_redirect": false
},
}
- HTTP Request Body(
request_body)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
body_type |
string | N | Body type, that is, the value of the request header Content-Type |
body |
string | N | Request Body |
form |
map[string]string | N | When the Content-Type is multipart/form-data, it is the form data of the request Body |
request_body example:
"advance_options": {
"request_body": {
"body_type": "multipart/form-data",
"body": "Fill in the request body, and pay attention to various complicated escapes here",
"form": {
"name": "file",
}
}
}
- HTTP Request Timeout (
request_timeout)
HTTP request timeout is mainly used to adjust the timeout of the HTTP request. The default timeout is 60 seconds, and the timeout can be adjusted here.
request_timeout example:
- HTTP Request a Certificate (
certificate)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ignore_server_certificate_error |
bool | N | Whether to ignore certificate errors |
private_key |
string | N | key |
certificate |
string | N | Certificate |
ca |
string | N | Temporarily unused |
certificate example:
"advance_options": {
"certificate": {
"ignore_server_certificate_error": false,
"private_key": "<your-private-key>",
"certificate": "<your-certificate-key>"
},
}
private_key example:
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxNn+/x
9WKHZvRf3lbLY7GAR/emacU=
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
Here is an example of certificate:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxWDR/+
InEHyg==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
Under Linux, this pair of keys can be generated by the following command:
- HTTP Request broker (
proxy)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
url |
string | N | The URL of the proxy, such as http://1.2.3.4:4321 |
headers |
map[string]string | N | Specify a set of headers on an HTTP request |
proxy example:
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"proxy": {
"url": "http://1.2.3.4:4321",
"headers": {
"X-proxy-header": "my-proxy-foobar"
}
}
},
}
post_script Definition¶
post_script is a Pipeline script used to evaluate the result of the test and extract variables from it.
inject variables¶
To facilitate the processing of HTTP responses by post_script and to enable the determination of test results and the extraction of variables, certain predefined variables can be utilized when composing the script. These are detailed as follows:
response: the response object of the HTTP request
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
status_code |
number | status code |
header |
json | response header {"header1": ["value1", "value2"]} |
body |
string | response body |
result: the test result
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
is_failed |
bool | failed or not |
error_message |
string | error message |
vars: the variable object to store the extracted variables
A JSON object where the key represents the variable name and the value represents the variable value. For example: vars["token"] = "123"
Example¶
body = load_json(response["body"])
if body["code"] == "200" {
result["is_failed"] = false
vars["token"] = body["token"]
} else {
result["is_failed"] = true
result["error_message"] = body["message"]
}
In the above example, the response content is initially parsed into a JSON object using load_json. Subsequently, it checks whether the response status code is 200. If it is, the token from the response content is extracted and assigned to the variable vars. If the status code is not 200, the is_failed attribute of result is set to true, and the error_message is assigned the message from the response content.
TCP Dial Test¶
Extra Field¶
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
host |
string | Y | TCP Host address |
port |
string | Y | TCP Port |
timeout |
string | N | TCP connection timeout |
message |
string | N | TCP message sent |
The complete JSON structure is as follows:
{
"TCP": [
{
"name": "tcp-test",
"host": "www.baidu.com",
"port": "80",
"message": "hello",
"timeout": "10ms",
"enable_traceroute": true,
"post_url": "https://<your-dataway-host>?token=<your-token>",
"status": "OK",
"frequency": "60s",
"success_when_logic": "and",
"success_when": [
{
"response_time":[
{
"is_contain_dns": true,
"target": "10ms"
}
],
"response_message": [
{
"is": "hello"
}
],
"hops": [
{
"op": "eq",
"target": 20
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
success_when Definition¶
- TCP Response Time Determination (
response_time)
response_time is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
target |
string | Y | Determining whether the response time is less than the value |
is_contain_dns |
bool | N | Indicates whether the response time includes DNS resolution time |
- Return a message decision (
response_message)
response_message is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
is |
string | N | Whether the returned message is equal to the specified field |
is_not |
string | N | Whether the returned message is not equal to the specified field |
match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned message contains a substring of the matching regular expression |
not_match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned message does not contain a substring of the matching regular expression |
contains |
string | N | Whether the returned message contains the specified substring |
not_contains |
string | N | Whether the returned message does not contain the specified substring |
for example:
- Network hop count (
hops)
hops is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
op |
string | Y | Compare relation, retrievable eq(=),lt(<),leq(<=),gt(>),geq(>=) |
target |
float | Y | Decision value |
ICMP Dial Test¶
Extra Field¶
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
host |
string | Y | Host address |
packet_count |
int | N | Number of ICMP packets sent |
timeout |
string | N | Connection timeout |
The complete JSON structure is as follows:
{
"ICMP": [
{
"name": "icmp-test",
"host": "www.baidu.com",
"timeout": "10ms",
"packet_count": 3,
"enable_traceroute": true,
"post_url": "https://<your-dataway-host>?token=<your-token>",
"status": "OK",
"frequency": "10s",
"success_when_logic": "and",
"success_when": [
{
"response_time": [
{
"func": "avg",
"op": "leq",
"target": "50ms"
}
],
"packet_loss_percent": [
{
"op": "leq",
"target": 20
}
],
"hops": [
{
"op": "eq",
"target": 20
}
],
"packets": [
{
"op": "geq",
"target": 1
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
success_when Definition¶
- ICMP packet loss rate (
packet_loss_percent)
Fill in the specific value as an array object, and each object parameter is as follows:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
op |
string | Y | Compare relationship retrievable eq(=),lt(<),leq(<=),gt(>),geq(>=) |
target |
float | Y | Decision value |
- ICMP response time (
response_time)
Fill in the specific time as an array object, and each object parameter is as follows:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
func |
string | Y | Statistical type, take the value avg,min,max,std |
op |
string | Y | Comparison relation, take value eq(=),lt(<),leq(<=),gt(>),geq(>=) |
target |
string | Y | Decision value |
- Network hop count (
hops)
hops is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
op |
string | Y | Compare relationships, retrievable eq(=),lt(<),leq(<=),gt(>),geq(>=) |
target |
float | Y | Decision value |
- Number of packets grabbed (
packets)
packets is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
op |
string | Y | Compare relationship retrievable eq(=),lt(<),leq(<=),gt(>),geq(>=) |
target |
float | Y | Decision value |
WEBSOCKET Dial Test¶
Extra Field¶
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
url |
string | Y | Websocket connection address, such as ws://localhost:8080 |
message |
string | Y | Websocket message sent after successful connection |
The complete JSON structure is as follows:
{
"WEBSOCKET": [
{
"name": "websocket-test",
"url": "ws://localhost:8080",
"message": "hello",
"post_url": "https://<your-dataway-host>?token=<your-token>",
"status": "OK",
"frequency": "10s",
"success_when_logic": "and",
"success_when": [
{
"response_time": [
{
"is_contain_dns": true,
"target": "10ms"
}
],
"response_message": [
{
"is": "hello1"
}
],
"header": {
"status": [
{
"is": "ok"
}
]
}
}
],
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"timeout": "10s",
"headers": {
"x-token": "aaaaaaa",
"x-header": "111111"
}
},
"auth": {
"username": "admin",
"password": "123456"
}
}
}
]
}
success_when Definition¶
- Response time judgment (
response_time)
response_time is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
target |
string | Y | Determining whether the response time is less than the value |
is_contain_dns |
bool | N | Indicates whether the response time includes DNS resolution time |
- Return a message decision (
response_message)
response_message is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
is |
string | N | Whether the returned message is equal to the specified field |
is_not |
string | N | Whether the returned message is not equal to the specified field |
match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned message contains a substring of the matching regular expression |
not_match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned message does not contain a substring of the matching regular expression |
contains |
string | N | Whether the returned message contains the specified substring |
not_contains |
string | N | Whether the returned message does not contain the specified substring |
for example:
- Request to return header judgment(
header)
header is a dictionary type object whose value for each object element is an array object with the following parameters:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
is |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field is equal to the specified value |
is_not |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field is not equal to the specified value |
match_regex |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field contains a substring of the matching regular expression |
not_match_regex |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field does not contain a substring of the matching regular expression |
contains |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field contains the specified substring |
not_contains |
string | N | The header returned specifies whether the field does not contain the specified substring |
for example:
advance_options Definition¶
- Request option (
request_options)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
timeout |
string | N | Connection timeout |
headers |
map[string]string | N | Specify a set of headers on request |
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"timeout": "30ms",
"headers": {
"X-Token": "xxxxxxxxxx"
}
},
}
- Authentication information (
auth)
Support for common user name and password authentication (Basic access authentication)。
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
username |
string | Y | user name |
password |
string | Y | user name and password |
GRPC Dial Test¶
Extra Field¶
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
server |
string | Y | gRPC server address, such as localhost:50051 |
post_script |
string | N | Pipeline script for result judgment |
Note: gRPC dial testing only supports unary RPC, streaming RPC is not supported.
The complete JSON structure is as follows:
{
"GRPC": [
{
"name": "grpc-test",
"server": "localhost:50051",
"post_url": "https://<your-dataway-host>?token=<your-token>",
"status": "OK",
"frequency": "5m",
"success_when_logic": "and",
"success_when": [
{
"body": [
{
"contains": "success"
}
],
"response_time": "500ms"
}
],
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"request_timeout": "10s",
"metadata": {
"x-token": "test-token"
},
"proto_files": {
"protofiles": {
"greeter.proto": "syntax = \"proto3\";\n\npackage greeter;\n\noption go_package = \"datakittest/grpc/pb\";\n\nimport \"pb/common.proto\";\n\nservice Greeter {\n rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (common.result) {}\n}\n\nmessage HelloRequest {\n string name = 1;\n}",
"pb/common.proto": "syntax = \"proto3\";\n\npackage common;\n\noption go_package = \"datakittest/grpc/pb\";\n\nmessage result {\n int32 code = 1;\n string msg = 2;\n}"
},
"full_method": "greeter.Greeter/SayHello",
"request": "{\"name\": \"world\"}"
}
},
"certificate": {
"ignore_server_certificate_error": false
}
},
"post_script": "..."
}
]
}
success_when Definition¶
- gRPC Response Body Judgment (
body)
body is an array object with the following parameters for each object:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
is |
string | N | Whether the returned body is equal to the specified field |
is_not |
string | N | Whether the returned body is not equal to the specified field |
match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned body contains a substring of the matching regular expression |
not_match_regex |
string | N | Whether the returned body does not contain a substring of the matching regular expression |
contains |
string | N | Whether the returned body contains the specified substring |
not_contains |
string | N | Whether the returned body does not contain the specified substring |
for example:
- gRPC Response Time Judgment (
response_time)
Fill in a specific time value. If the response time of the request is less than the specified value, the dialing test is judged to be successful, such as:
Note that the time units specified here are
ns(nanoseconds)/us(microseconds) /ms(milliseconds) /s(seconds) /m(minutes) /h(hours). For gRPC dial testing,msorsunits are generally used.
advance_options Definition¶
- Request Option (
request_options)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
request_timeout |
string | N | Request timeout, default is 30s |
metadata |
map[string]string | N | gRPC request metadata (metadata) |
proto_files |
object | N | Discover methods through proto files (choose one of proto_files, reflection, health_check) |
reflection |
object | N | Discover methods through gRPC reflection (choose one of proto_files, reflection, health_check) |
health_check |
object | N | Use gRPC health check service (choose one of proto_files, reflection, health_check) |
proto_files object definition:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
protofiles |
map[string]string | Y | Proto file content, key is the file reference path (main file is the file name, imported files must match the path in the import statement), value is the file content |
full_method |
string | Y | Full method name, format is ServiceName/MethodName |
request |
string | N | Request body in JSON format |
reflection object definition:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
full_method |
string | Y | Full method name, format is ServiceName/MethodName |
request |
string | N | Request body in JSON format |
health_check object definition:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
service |
string | N | Service name to check, empty means check the entire service |
request_options example:
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"request_timeout": "10s",
"metadata": {
"x-token": "test-token",
},
"proto_files": {
"protofiles": {
"greeter.proto": "syntax = \"proto3\";\n\npackage greeter;\n\noption go_package = \"datakittest/grpc/pb\";\n\nimport \"pb/common.proto\";\n\nservice Greeter {\n rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (common.result) {}\n}\n\nmessage HelloRequest {\n string name = 1;\n}",
"pb/common.proto": "syntax = \"proto3\";\n\npackage common;\n\noption go_package = \"datakittest/grpc/pb\";\n\nmessage result {\n int32 code = 1;\n string msg = 2;\n}"
},
"full_method": "greeter.Greeter/SayHello",
"request": "{\"name\": \"world\"}"
}
}
}
Or use reflection:
Note: Using reflection requires the gRPC server to enable gRPC Server Reflection service.
"advance_options": {
"request_options": {
"reflection": {
"full_method": "greeter.Greeter/SayHello",
"request": "{\"name\": \"world\"}"
}
}
}
Or use health check:
Note: Using health check requires the gRPC server to implement the gRPC Health Checking Protocol service.
- Certificate Configuration (
certificate)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ignore_server_certificate_error |
bool | N | Whether to skip server certificate verification (do not verify the validity of the server certificate) |
private_key |
string | N | Client private key (for mTLS) |
certificate |
string | N | Client certificate (for mTLS) |
ca |
string | N | CA certificate (for verifying server certificate) |
certificate example:
"advance_options": {
"certificate": {
"ignore_server_certificate_error": false,
"ca": "<your-ca-cert>",
"private_key": "<your-private-key>",
"certificate": "<your-certificate>"
}
}
- Security Options (
secret)
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
not_save |
bool | N | Whether not to save response body content |
secret example:
post_script Definition¶
post_script is a Pipeline script used to evaluate the result of the test.
Inject Variables
To facilitate the processing of gRPC responses by post_script and to enable the determination of test results, certain predefined variables can be utilized when composing the script. These are detailed as follows:
response: Response object
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
body |
string | Response content (JSON format string) |
result: Test result
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
is_failed |
bool | Failed or not |
error_message |
string | Error message |
Example
body = load_json(response["body"])
if body["message"] == "Hello world" {
result["is_failed"] = false
} else {
result["is_failed"] = true
result["error_message"] = "Unexpected response"
}
In the above example, the response content (response["body"]) is initially parsed into a JSON object using load_json. Subsequently, it checks whether the message field in the response is "Hello world". If it is, the is_failed attribute of result is set to false. If the message is not "Hello world", the is_failed attribute of result is set to true, and the error_message is assigned the error message.
Multi-Step Dial Test¶
Multi-step dial testing allows you to define a sequence of dial test steps that are executed in order. It supports HTTP requests and wait operations, and can pass variables between steps.
Additional fields:
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
steps |
array | Y | List of dial test steps, must contain at least one step |
The overall JSON structure is as follows:
{
"MULTI": [
{
"name": "multi-step-test",
"status": "OK",
"post_url": "https://<your-dataway-host>?token=<your-token>",
"frequency": "10s",
"steps": [
{
"type": "http",
"name": "step1",
"task": "{\"name\": \"step1\", \"method\": \"GET\", \"url\": \"http://api.example.com/resource\", \"post_script\": \"vars[\\\"token\\\"] = \\\"token_value\\\"\"}",
"allow_failure": false,
"retry": {
"retry": 3,
"interval": 1000
},
"extracted_vars": [
{
"name": "token",
"field": "token",
"secure": false
}
]
},
{
"type": "wait",
"name": "step2",
"value": 5
},
{
"type": "http",
"name": "step3",
"task": "{\"name\": \"step3\", \"method\": \"POST\", \"url\": \"http://127.0.0.1:9000?token={{token}}\", \"post_script\":\"result[\\\"is_failed\\\"]=true\"}",
"allow_failure": false
}
]
}
]
}
steps Definition¶
steps is an array of dial test steps. Each step can be one of the following two types:
- HTTP Step (
type: "http")
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Y | Step type, must be http |
name |
string | Y | Step name |
task |
string | Y | JSON string of the HTTP dial test task |
allow_failure |
bool | N | Whether to allow the step to fail, default is false |
retry |
object | N | Retry configuration, see below for details |
extracted_vars |
array | N | List of extracted variables for use in subsequent steps |
- Wait Step (
type: "wait")
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Y | Step type, must be wait |
name |
string | Y | Step name |
value |
int | Y | Wait time in seconds |
allow_failure |
bool | N | Whether to allow the step to fail, default is false |
retry Definition¶
Retry configuration is used to set the retry strategy when a step fails.
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
retry |
int | Y | Number of retries, must be between 0-5 |
interval |
int | Y | Retry interval in milliseconds, must be between 0-5000 |
extracted_vars Definition¶
Extract variables from the vars defined in the HTTP post_script for template substitution in subsequent steps.
| Field | Type | Whether Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
string | Y | Variable name used for template substitution in subsequent steps |
field |
string | Y | Variable name defined in vars |
secure |
bool | N | Whether it is a secure variable. Secure variables will not be displayed in results |
Template Function Usage Instructions¶
When defining a monitoring task, you are allowed to embed template variables in strings.
Function List¶
The following template functions are currently supported:
timestampfunction: Generate a timestamp
Returns the timestamp of the current UTC time, supporting multiple time units (s, ms, us, ns). It returns 0 by default (when the unit parameter is invalid).
Usage example:
datefunction: Format time string
Returns the string of the current local time according to the specified format, supporting two definition formats (rfc3339, iso8601).
Usage examples:
urlencodefunction: URL encoding
Performs URL encoding on the input string (in compliance with the application/x-www-form-urlencoded specification), which is used to handle special characters in URLs.
Usage example:
Instructions for Nested Use of Functions¶
Template functions support nested use, which means the return value of one function can be used as the parameter of another function.
Usage example: