Timeseries Chart¶
Timeseries charts are generally used to show the trend changes of data at equal time intervals, and can be used to analyze the effect and impact of multiple sets of metric data.
Use Cases¶
- View trends in application performance metrics data over time, such as the number of application "requests" over the last 15 minutes;
-
View trends in user access metrics data over time, such as the occurrence of user access "errors" over different time frames;
-
View similar trending metrics over a fixed time frame;
- View events triggered by abnormal data fluctuations.
Chart Query¶
Simple Query, Expression Query, DQL Query, and Promql Query are supported; simple query is added by default. Each query presets 5 types of return result quantities, including 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, with 20 pieces of data returned by default, and supports manual entry, up to a maximum of 100 pieces of data.
For more detailed descriptions of the chart query conditions, see Chart Query.
Chart Link¶
Links can help to achieve a transition from the current chart to the target page. You can add internal links within the platform or external links, and can modify the corresponding variable values in the link through the template variables to send the data information over, achieving data linkage.
For more related setting descriptions, see Chart Link.
Event Association¶
By adding filtering fields, match abnormal events related to the selected fields, thereby achieving the purpose of displaying the association of time-series data and events. This function can help you perceive whether there are related events during the data fluctuation while viewing trends, to help you locate problems from another perspective.
For more related setting descriptions, see Event Association.
Basic Settings¶
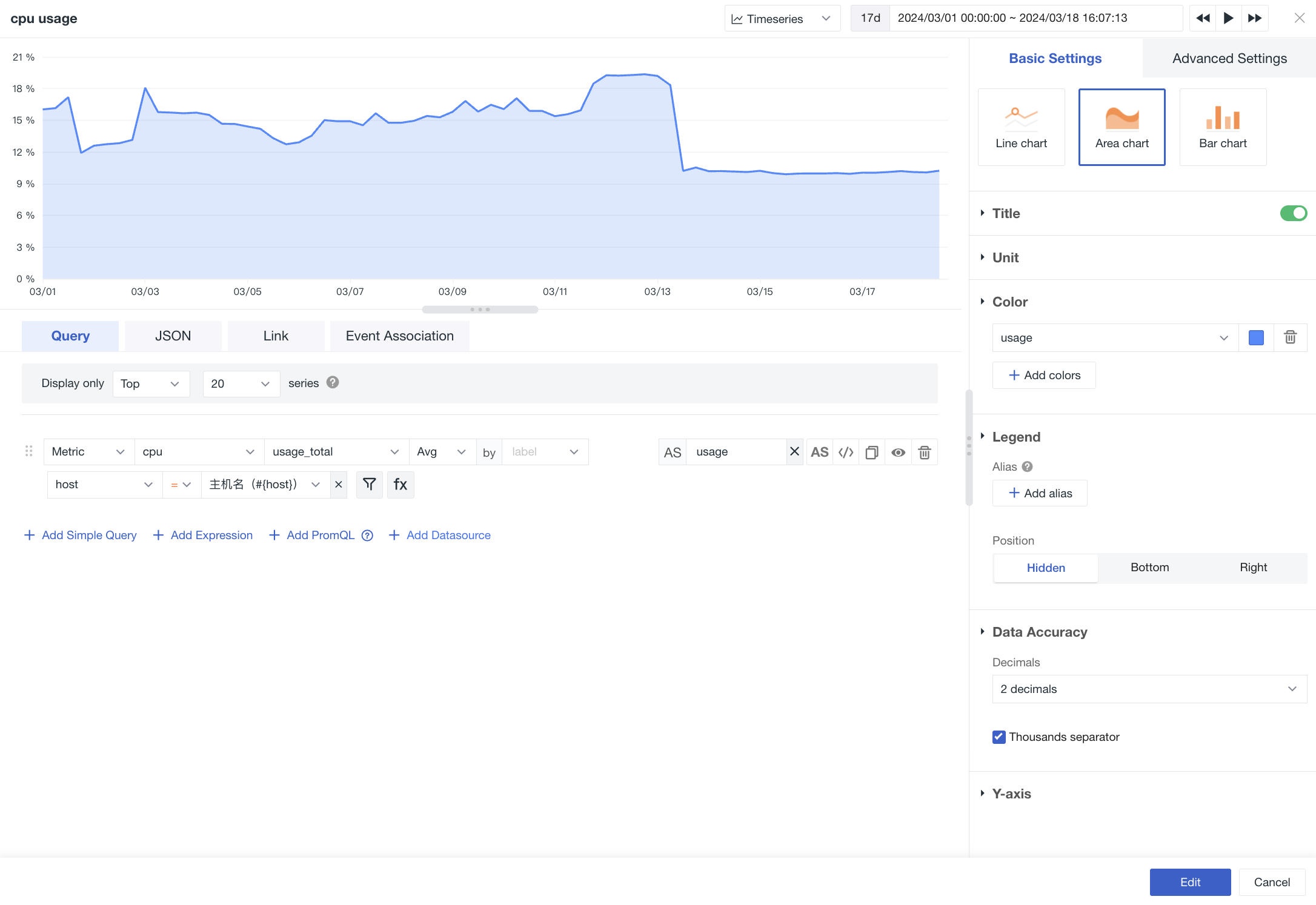
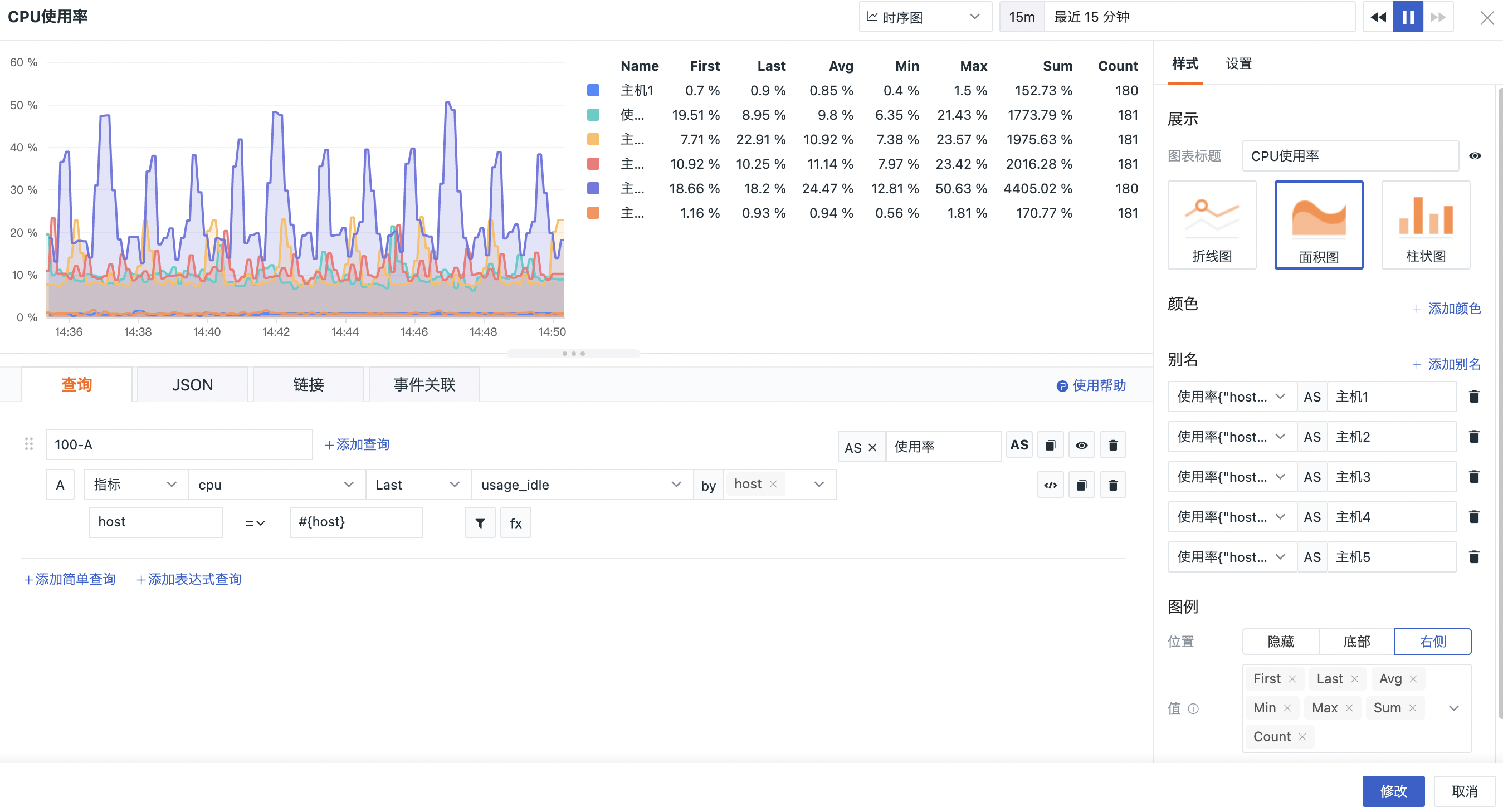
The chart types include line chart, bar chart, and area chart (line chart is selected by default).
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | Set a title for the chart. After setting, it will be displayed in the upper left corner of the chart, and can be hidden. |
| Description | Add a description for the chart. After setting, an "i" tip will appear behind the chart title. If not set, it will not be displayed. |
| Stacking | Only supports bar charts, turned off by default. |
| Unit | Default unit display: After configuring the unit: It will give priority to your custom configured unit for display, and metric data supports two options for numerical values: Scientific Notation Explanation Default rounding: The units are ten thousand, million, such as 10,000 is displayed as 1 ten thousand, 1,000,000 is displayed as 1 million. Keep two decimal places; Short scale: Units are K, M, B. That is, thousand, million, billion, trillion are used to represent thousand, million, billion, and trillion in Chinese context. For example, 1000 is 1k, 10,000 is 10k, 1,000,000 is 1 million. Keep two decimal places. |
| Color | Set the display color of the chart data, support custom manual input of preset colors, input format is: aggregate function (metric) {"Label": "Label Value"}, such as last(usage_idle){"host": "guance_01"}. |
| Legend | For more details, please refer to Legend Description. |
| Data Format | You can choose the Decimal Places and Thousand Separator. |
| Y Axis | Support customizing the maximum and minimum values of the Y axis. |
Advanced Settings¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
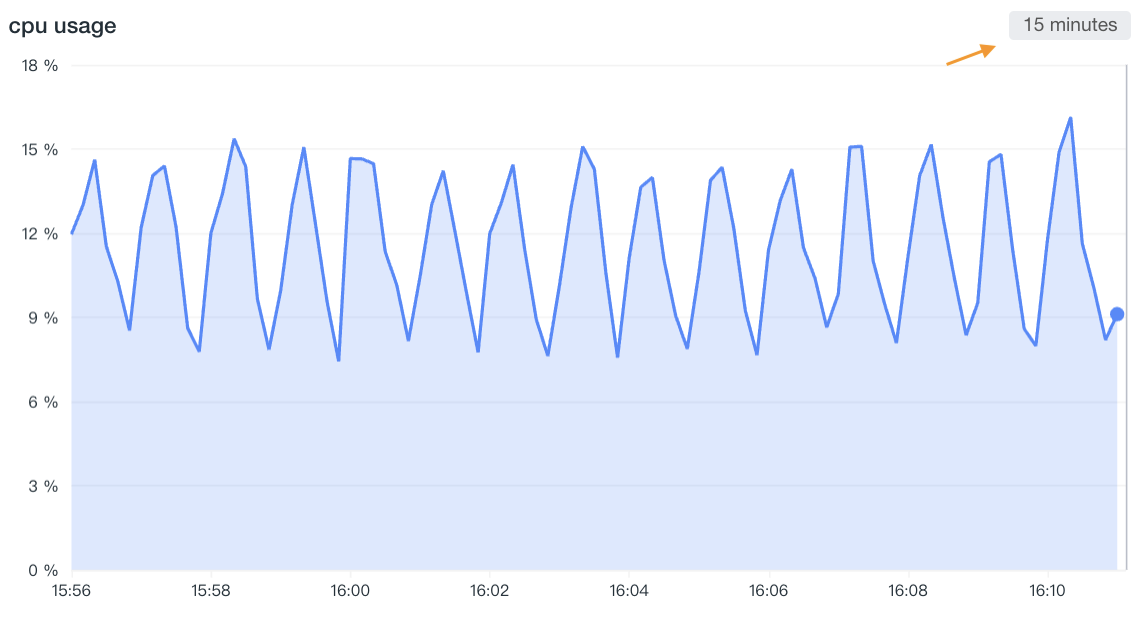
| Lock Time | That is, fix the time range of the current chart query data, not subject to the restriction of the global time component. After setting, the user-defined time will appear in the upper right corner of the chart, such as "xx minutes", "xx hours", "xx days". (See the table below Figure 1.) |
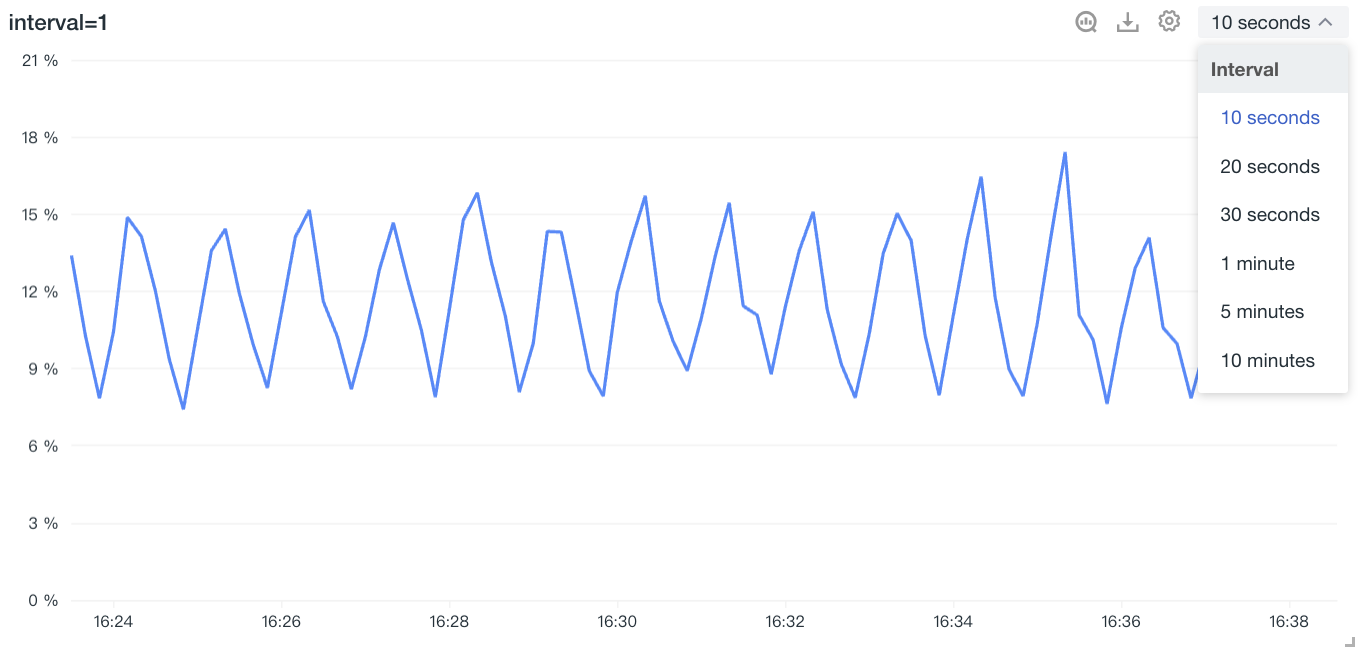
| Interval | That is, the calculation interval (interval) of the chart query data. (See the table below Figure 2.) interval, and adjust the interval according to the "time range/maximum number of points" if it conflicts with the "maximum number of return points". It includes 10 seconds, 20 seconds, 30 seconds, 1 minute, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 6 hours, 12 hours, 1 day, 7 days, and 30 days. (The effect is shown in the table below Figure 3.) |
| Maximum Return Points | That is, the maximum number of data points for each series, you can enter any integer between 2-1000. If you have not customized it, the maximum point limit is 720 by default. Based on the selected time interval, if the query range is too large and exceeds the maximum number of points, the Based on the selected time interval, if the query range is too large and exceeds the maximum number of points, the interval will be calculated according to the maximum number of points and the data will be returned in rounded form. |
| Collapsed Blend | Only exist in bar charts. |
| Contemporary Comparison | Compare with the same period of the previous time. By default, it is shown as closed. After turning on the same period comparison, the comparison dimension supports 4 options: hour (compared with an hour ago), day (compared with a day ago), week (compared with a week ago), month (compared with a month ago). Multiple selections are supported, for more details, see Same Period Comparison. |
| Baseline | Support adding baseline values, baseline titles, and baseline colors. |
| Field Mapping | Work with the object mapping function of view variables, turned off by default, if object mapping is configured in view variables: |
| Data Authorization | The list of authorized workspaces; after selection, you can query and display the workspace data through the chart. |
| Data Sampling | Only for Doris log data engine workspace; after turning on, it will sample query data other than "metrics". The sampling rate is not fixed and will adjust dynamically according to the amount of data. |
Figure Examples:
Chart Analysis¶
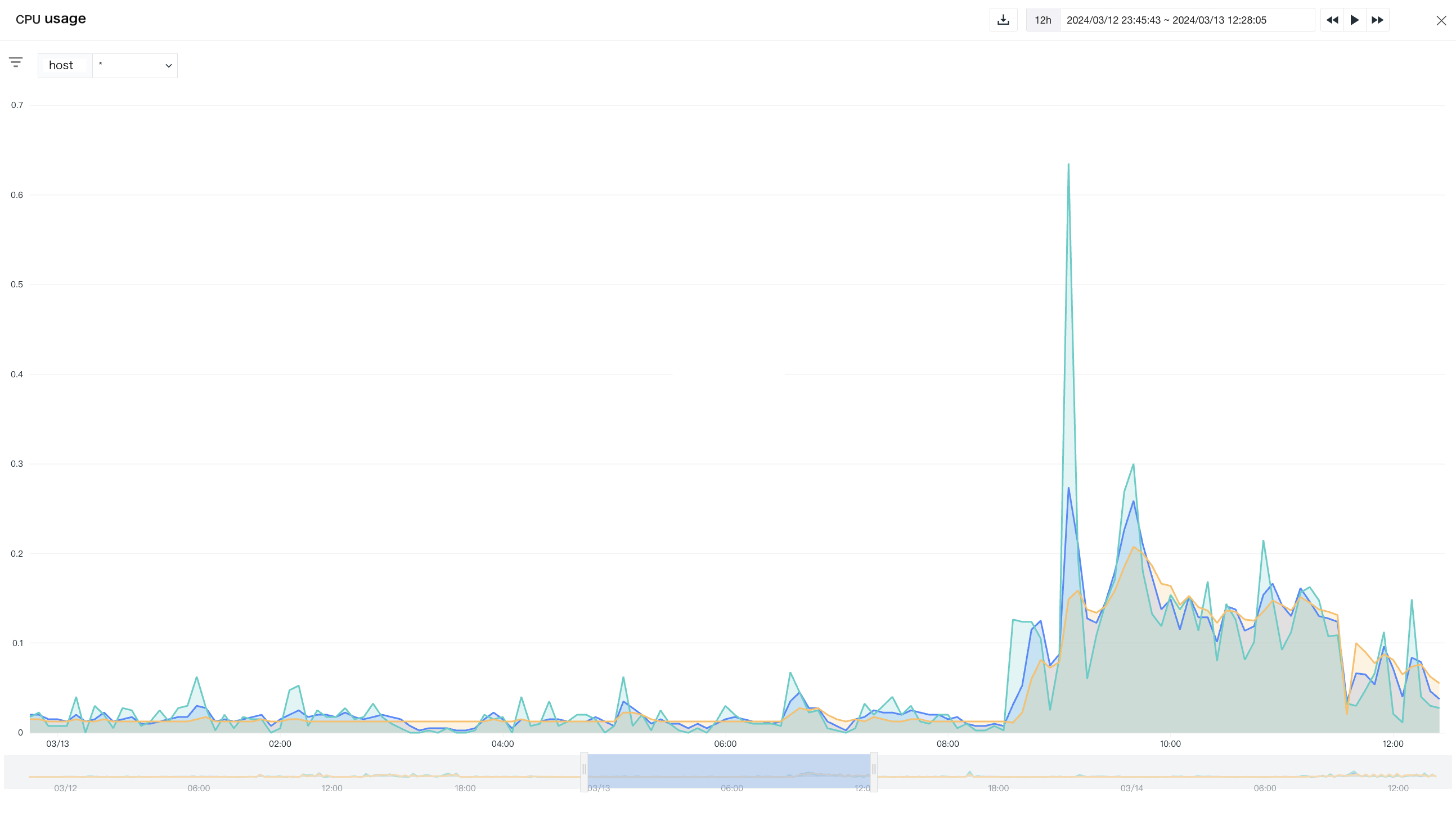
A time series chart is a two-dimensional chart indexed in chronological order, with the horizontal axis representing time and the vertical axis representing data. Based on the selected time range, the time series chart will plot the trend of object data within this time range.
Note: A time series chart returns up to 10 timelines for a single query statement, i.e., based on the results of the group by condition, data exceeding 10 timelines is displayed in order, showing only 10 timelines.
Timeline Functions¶
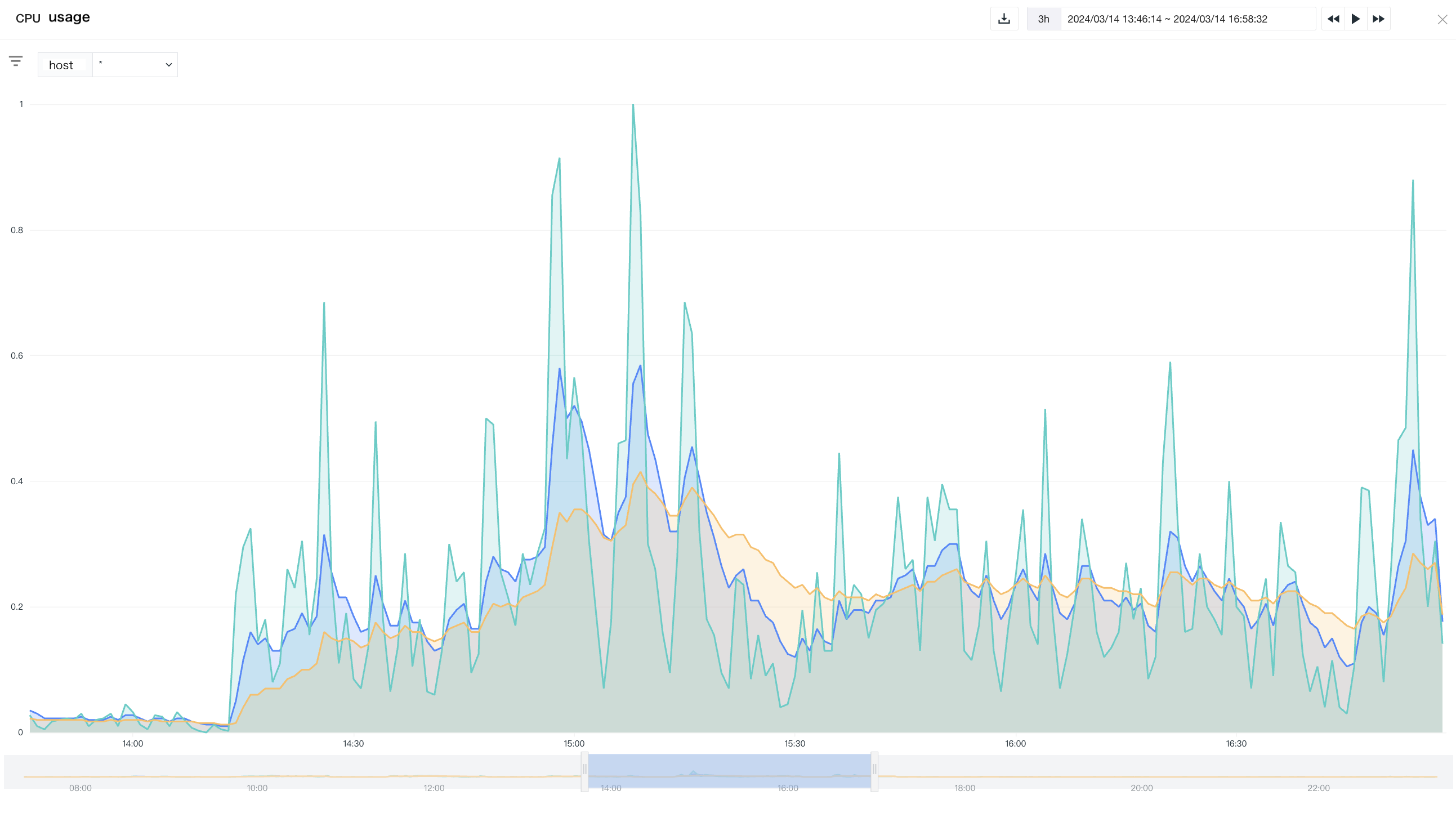
In addition, in analysis mode, Guance provides a timeline function, which means that you can not only preview the interaction changes of object data and time through the timeline under the chart, but also drag to select the display time range. The timeline range is based on the selected time range as the query cycle, fixed three query cycles forward, and up to one query cycle backward (up to the current time point).
Example: If the current time point is 11:33 and the time range is selected as [Last 1 hour], then the timeline range is [10:33 - 11:33].
Similar Trend Metrics¶
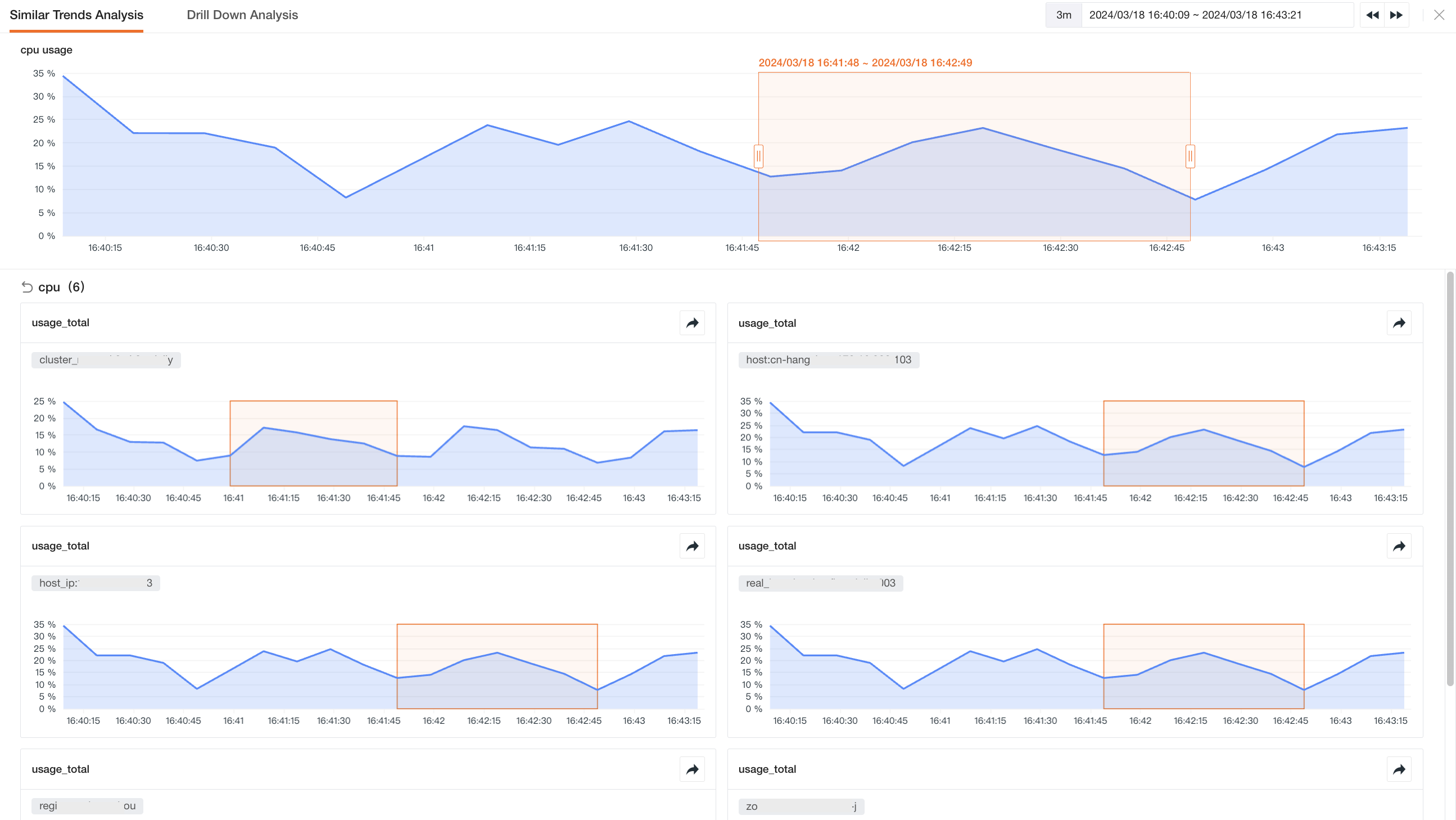
In the analysis mode of the time series chart, when you select the trend line/bar of the time series chart, you can view similar trend metrics.
Viewing similar trend metrics is based on the time range you have selected as absolute time, querying similar trend metrics within the space. You can:
- On the time series chart, click the chart and drag the mouse to select the search time range;
- Click the "button" to search for similar trend results;
- Click the query result to enter the "similar trend metric" details page.
Similar Trend Results¶
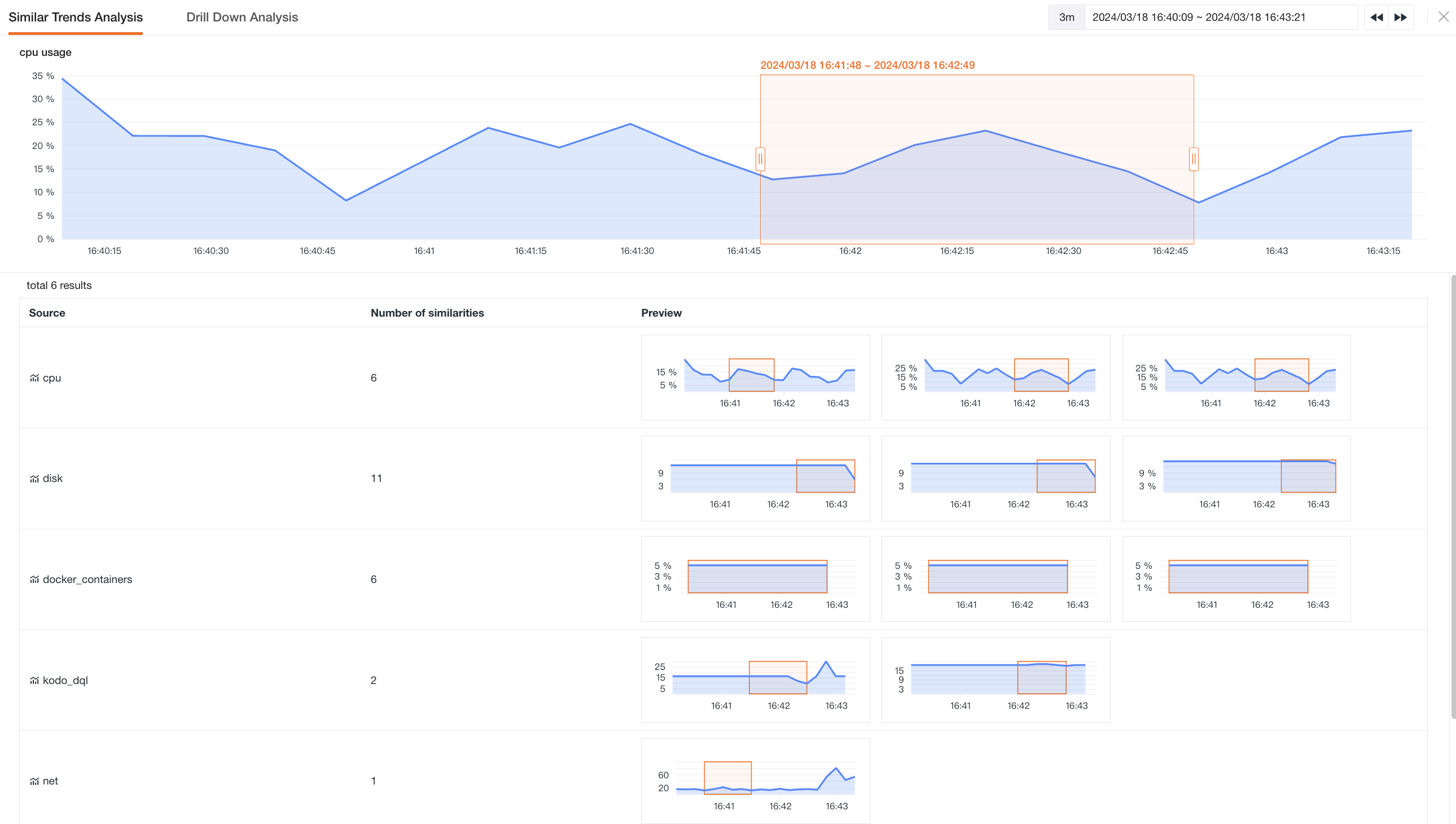
Based on the selected absolute time range, the query result list includes:
- Source: The set of metrics with similar trends;
- Similar Quantity: The number of charts with similar trends under the corresponding "measurement";
- Preview: A preview of the chart with similar trends.
Note:
-
When querying similar intervals, the currently selected time range is defaulted to Absolute Time, and will not be changed by any external influence or observer. If you need to change the time range, you need to adjust the time range again;
-
After entering the similar interval page, you can adjust the search time range by clicking and dragging the rectangle. If you have already selected a region, you can still move or adjust the selected time range;
-
After dragging to a new time range, you need to confirm/cancel the change of time range.
Legend¶
Alias: After adding an alias, the name of the legend will also change, making it easier to distinguish related metrics.
The alias supports the use of template variables for one-key replacement: for example:
-
{{tags}} means to replace with all "tag names" and "tag values";
-
{{host}} means to replace with the "tag value" of the host.
Example: Based on the metric, the setting of the alias will present the following scenarios:
Effect without adding an alias:
Effect of replacing with plain text input:
Input variable {tags}} based on by condition:
Note: When there is a by condition in your query, all returned legend series will be displayed for you.
Position: Currently supports the choice of hiding, bottom, right side legend (clicking on the index line in the legend can hide/show the corresponding index).
Display value: Choose the values or calculated values that you want to display in the legend.
The value of the time series chart legend will be aggregated again based on the chart query result, currently supports the selection of Last (the last value), First (the first value), Avg (average value), Min (minimum value), Max (maximum value), Sum (sum), Count (return points).
As shown in the figure below: First means to return the first value of the current time series chart query result, and Last is the last value of the current time series chart query result. Clicking on the legend value supports ascending and descending sorting.
Note: Avg , Sum , Count will display different results depending on the selected time interval (original interval and auto alignment).
Example¶
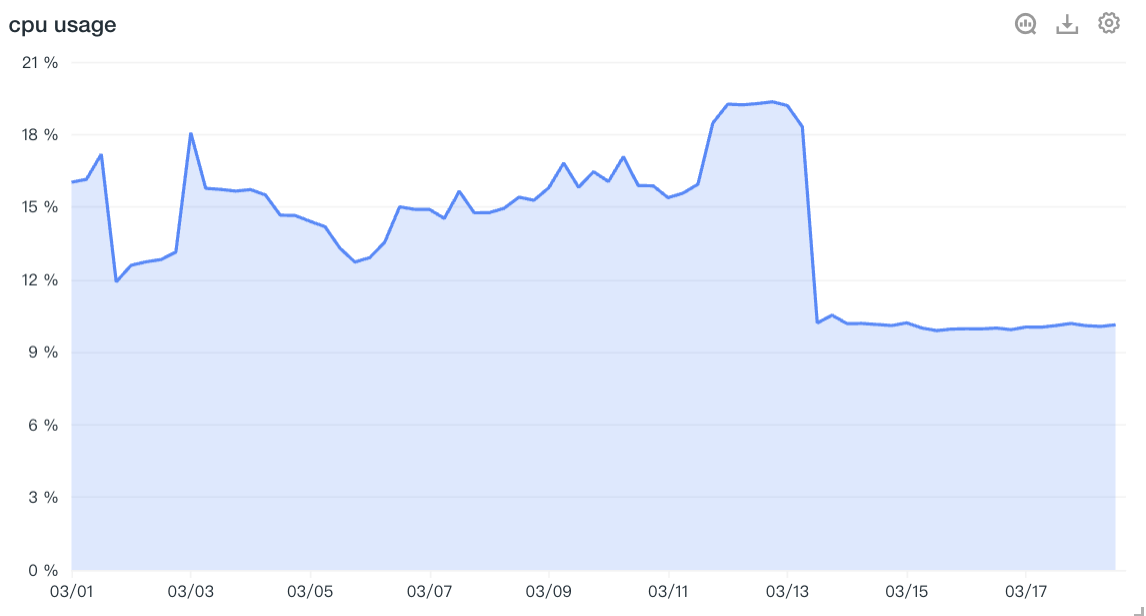
The following figure shows the trend changes of the CPU usage of the host in the last 15 minutes in line charts, bar charts, and area charts: