Log Index¶
By creating and managing multiple indexes, the system automatically archives log data into the corresponding index based on predefined filtering conditions. Additionally, you can customize a data storage strategy for each index to effectively control and reduce storage costs, achieving flexibility in data management and dual optimization of economic benefits.
Under the log index, you can:
Note
By default, multi-log indexes cannot be created, please contact your account manager to request activation of this feature.
Start Creating¶
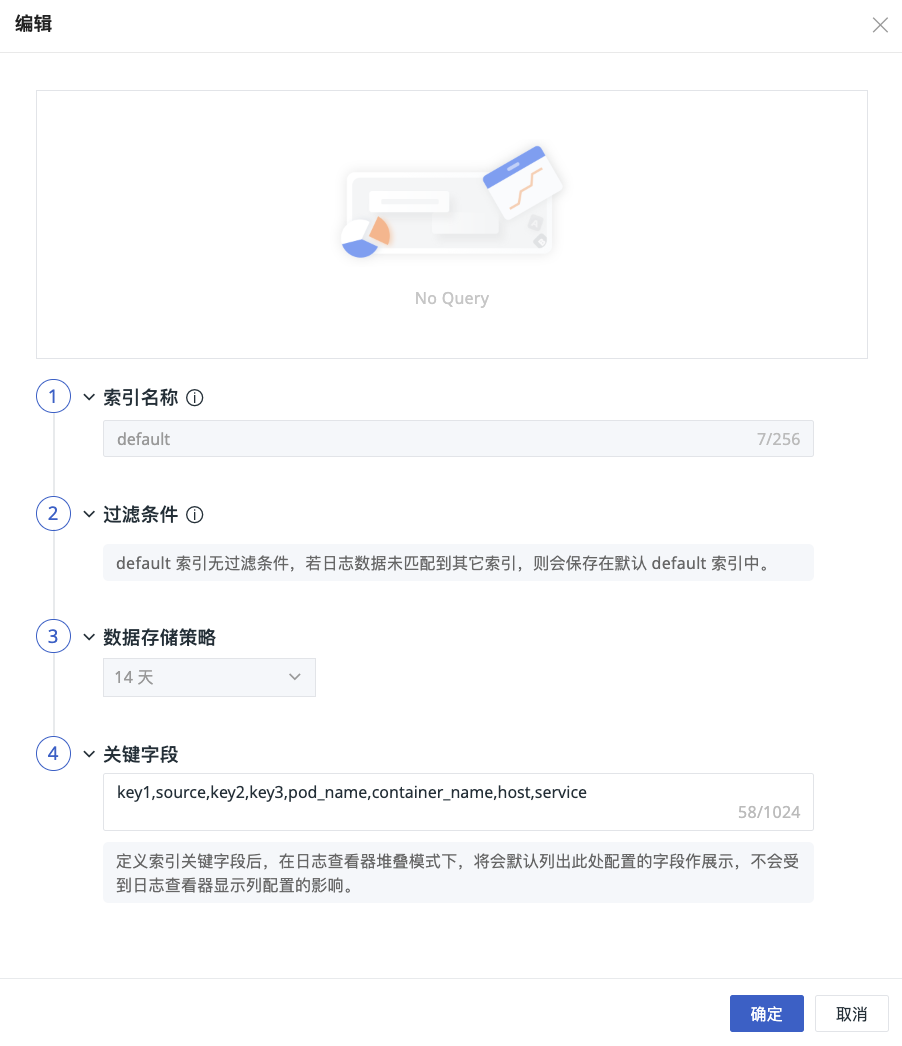
- Navigate to the Log > Index > Create Index page;
- Customize the name of the index;
- Add filtering conditions: supports
in,not inand other filtering methods; - Configure the data storage strategy, choose standard storage duration, low-frequency storage duration, and archive storage duration;
- Input key fields.
Note
Deployment Plan users can customize the data storage strategy duration here, range: 1d ~ 1800d.
Index Rules
- The index name must be unique, starting with a letter, containing only lowercase letters, numbers, or “_” characters, cannot be modified, and deleted index names cannot be recreated;
- Default index: all logs are stored by default in an index named
default, which only supports modifying key fields; - Log flow: after setting up multiple indexes, logs flow into the first matching index, and the same log will not be saved across indexes;
- Index quantity limit: including the
defaultindex, there can be at most 6 indexes, meaning custom indexes can be created up to 5 times; - Member permissions: standard members and read-only members have only viewing rights, while administrators and owners can edit, delete, and drag-and-drop sort.
Key Fields¶
Set exclusive key fields under the index dimension to ensure that the display of log data is unaffected by column configuration settings, ultimately appearing in the Log Explorer > Stacked Mode, facilitating efficient differentiation and analysis of data from different log indexes.
Definition Rules¶
- Use a comma
,as the delimiter; - Fields listed in
messageare configured as key fields in the index, formatted askey:value; ifvaluehas no value, it displays as “-”; - Log data with key fields configured in the index is unaffected by display items and applies only to the
messagecolumn.
One-Click Acquisition¶
- When data is archived to this index, click the button, and the system will automatically extract key fields from the latest day's reported data; the input box content will be overwritten by the newly obtained
key; - If there is no data reported for the current index, clicking the button will not change the content of the input box.
Note
If there are too many fields under the index, the input box will only extract the first 50 key fields.
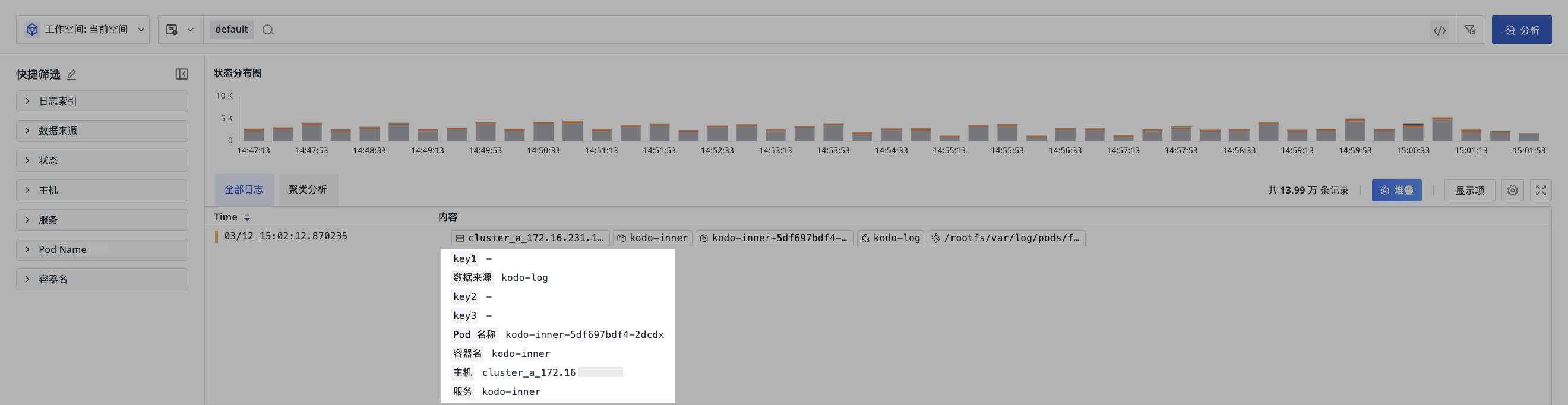
Display Example¶
- Define the key fields for
defaultaskey1,source,key2,key3,pod_name,container_name,host,service; - In the explorer, select to view data only from the
defaultindex; - The effect is shown in the following figure:
Bind External Index¶
After successful binding, you can query and analyze data from external indexes within the workspace.
Currently supported external indexes include:
SLS Logstore
Elasticsearch
OpenSearch
LogEase
Volcengine TLS
Note
- Bound indexes only support deletion; after unbinding, logs under that index cannot be queried;
- Other indexes cannot have the same name as log indexes or historical log indexes.
Field Mapping¶
Since Guance and external indexes may have inconsistent standard fields, we provide a field mapping function to ensure normal functionality.
To quickly view and analyze log data from external indexes in Guance, Guance provides a field mapping function, allowing direct mapping of log fields when binding external indexes.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
time |
The reporting time of the log, SLS Logstore maps date field to time by default, Elasticsearch and OpenSearch can fill in actual data; without this field, data in the log viewer will appear out of order. |
_docid |
The unique ID of the log. After mapping, you can view details of the bound log. If the original field is not unique, the log with the earliest timestamp is displayed after refreshing the detail page. Without this field, some content will be missing from the log detail page. |
message |
The content of the log. After mapping, you can view the content of the bound log and perform pattern analysis on log data through the message field. |
For more details, refer to Log Viewer Pattern Analysis.
You can also click Edit in the external index list to modify the field mapping of the index you need.
Note
- Mapping rules for each index do not share and are independently preserved;
- If a log contains a
_docidfield and another field is mapped to the same name, the original_docidin the log will not take effect.
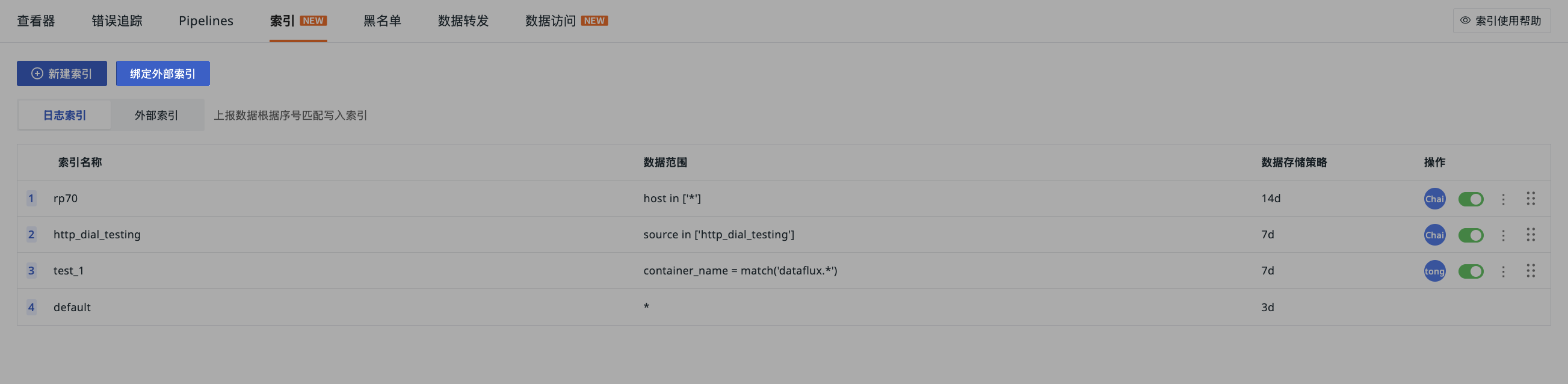
Manage Indexes¶
You can manage the index list via the following operations.
-
After disabling an index, subsequent logs will no longer enter that index and will continue to match and save in other indexes. If no other index matches, they will be saved in the default
defaultindex; -
After enabling an index, subsequent logs will re-enter and save in that index.
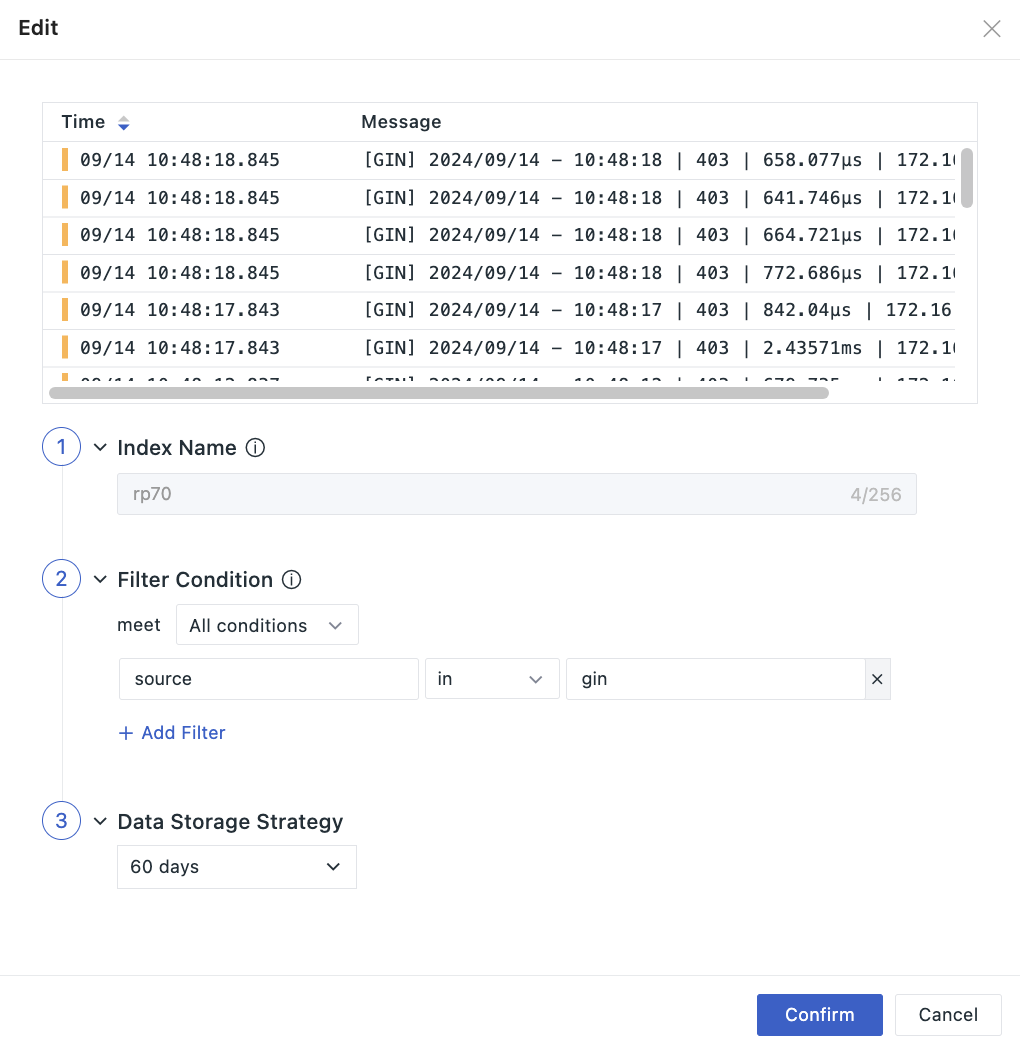
Click the Edit icon to edit the already created log index. In the figure below, after the current index index.da is successfully created, when log data with source as datakit is reported, it will match and save in the first matching index.
Note
Changing the storage strategy will delete data in the index, please proceed with caution.
Click to view all operation logs related to that index.
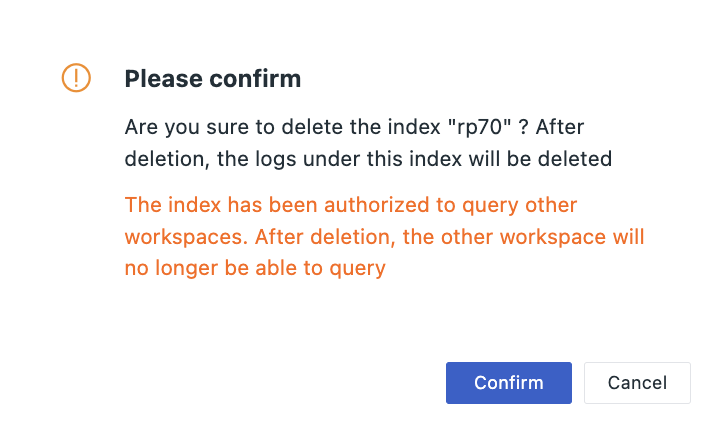
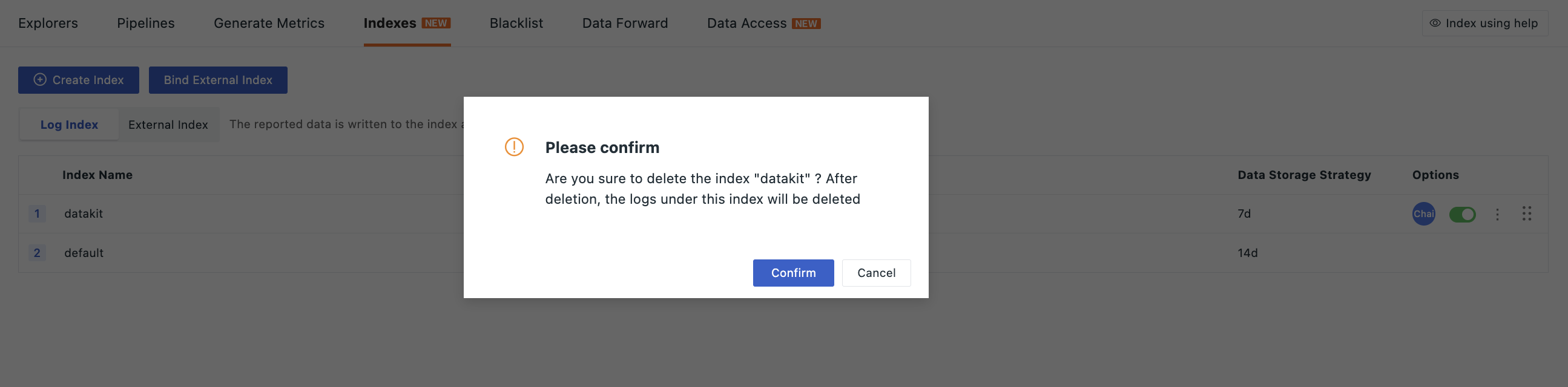
Click the icon to delete the created log index.
Note
After deletion, the log data in that index will also be deleted. If no other matching index exists, subsequently reported log data will be saved in the default default index.
If the deleted index was authorized for querying by other workspaces, after deletion, the other space will no longer be able to query that index.
After deleting a log index, you can recreate an index with the same name as needed.
Click the icon to drag and drop the already created log index up or down.
Note
Logs will flow into the first matched index, changing the index order might lead to changes in log flow.