Workspace Management¶
Workspaces are designed for multi-user environments and can isolate data from different units.
Create Workspace¶
In the workspace list, click Create Workspace in the top-right corner.
Workspace Information¶
-
Enter a workspace name;
-
Select the workspace language;
-
Select the workspace owner: has the highest operational permissions for the workspace;
- Optionally input a description for this workspace.
Main Storage Engine¶
Automatically lists the data storage engines.
If you do not select a data storage engine, the data will be saved to the system's main storage engine.
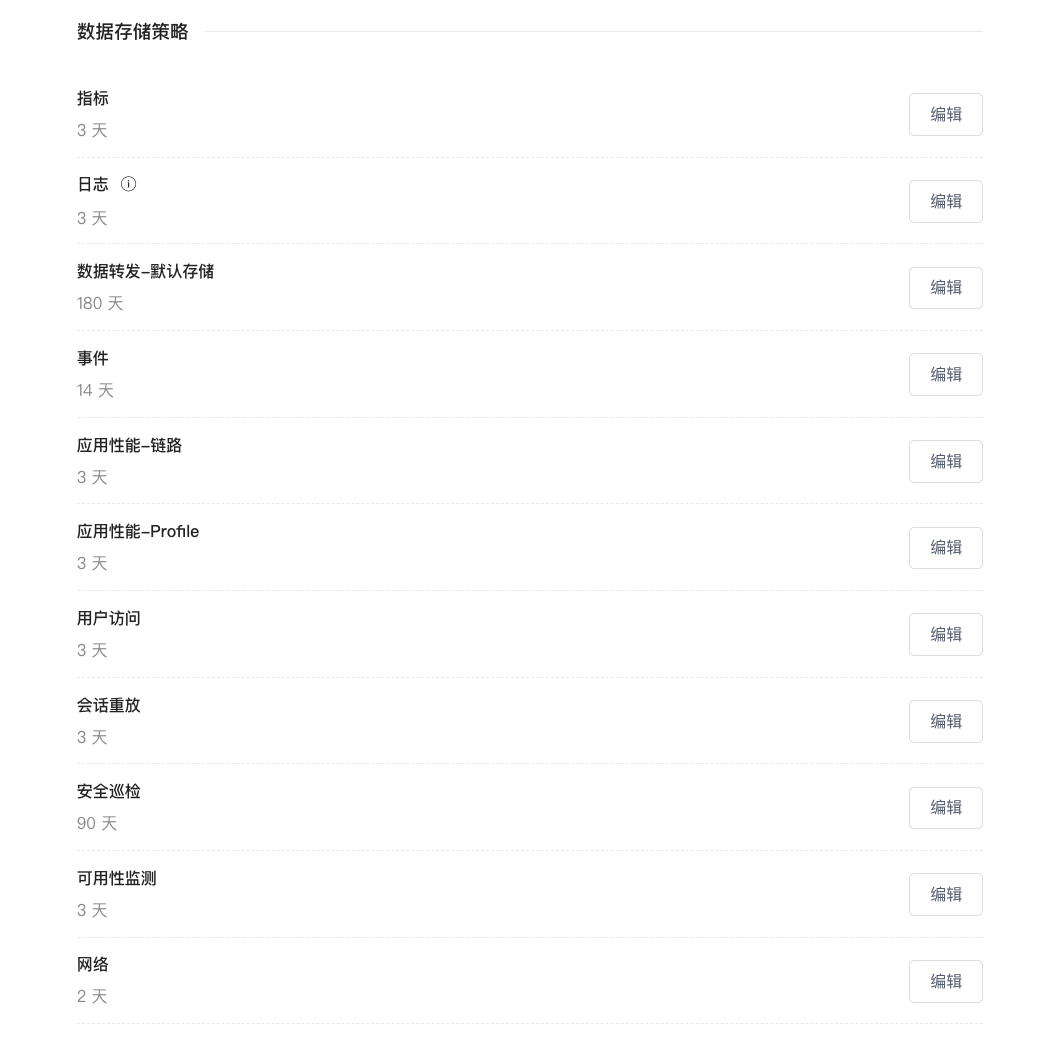
Data Retention Policy¶
This refers to the data retention period for the current workspace.
In addition to the storage durations corresponding to each data type, you can also choose to set a custom retention period (<= 1800 days).
Configuration of ultra-long retention periods
- When configuring ultra-long data retention periods for OpenSearch or Elasticsearch clusters, it is necessary to estimate the usage of storage space as well as the number of index shards;
- OpenSearch or Elasticsearch clusters default to a maximum of 1000 shards per node. For example, for a 3-node cluster, the total number of shards should not exceed 3000;
- Example of shard count calculation: Assume that the log index configuration for a certain workspace is 2 replicas, 3 shards per index, with each shard having a maximum size of 30GB, and daily data volume is approximately 180GB (i.e., 2 indices), with data retained for 200 days. The total shard count formula would be: Number of index replicas × Daily index count × Shards per index × Data retention days = 2 × 2 × 3 × 200 = 2400 shards;
- If there are multiple workspaces, the index shard counts of all workspaces need to be aggregated, and at the same time, the shard counts of other data types indexes need to be estimated.
Others¶
-
Left-star query: Determines if the newly created workspace supports left-star queries;
-
Custom mapping rules: Enabling this configuration allows the corresponding workspace to customize mapping rules. The priority of custom mapping rules in a workspace is higher than the mapping rules in the management backend.
Note
If you configure overlapping mappings in both the management backend and within the workspace, the member role will be the combined set of roles assigned by the management backend and the workspace.
-
Custom log indices: Once enabled, this allows the workspace to create multiple index strategies for storing logs;
-
Ultra-large log counting unit: Used to set the counting unit for ultra-large logs, which can split large logs into multiple entries for billing purposes according to the set counting unit;
-
Query quantity limit: Customize query limits for different user workspaces to prevent performance degradation due to excessive query volumes, ensuring optimal product experience. After setting a query limit, any excess queries must be performed again.
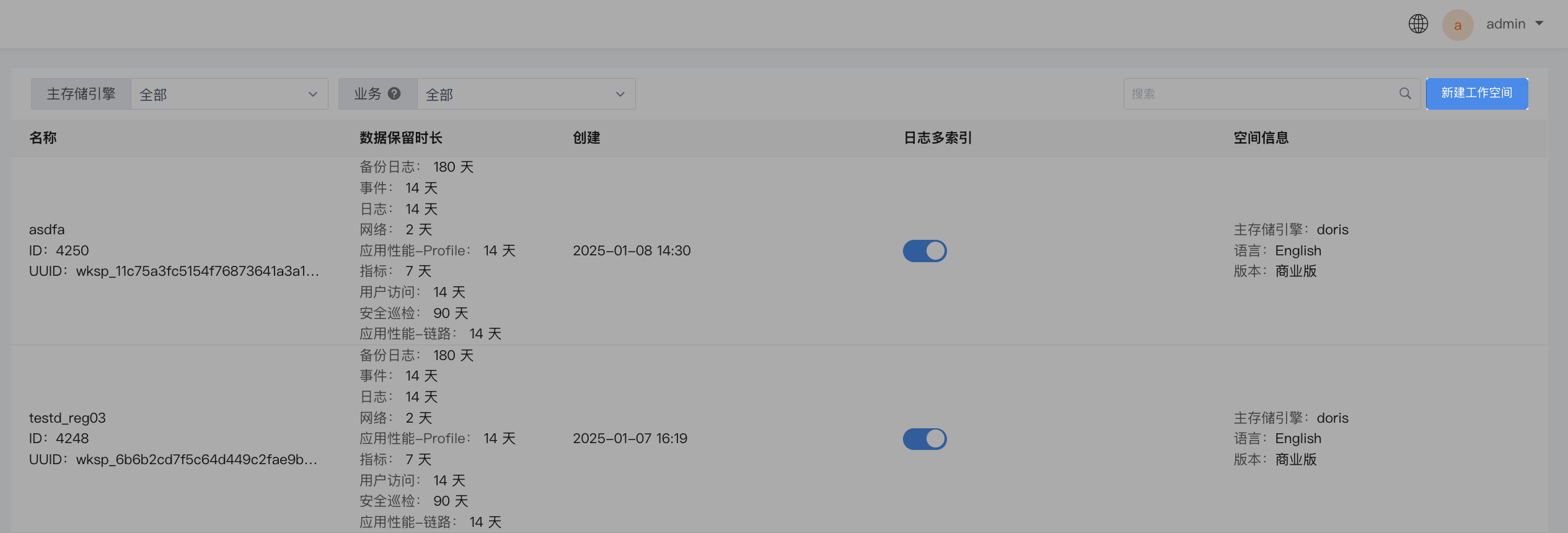
Manage Workspaces¶
Filtering¶
Quickly filter and locate workspaces using two filters: Main Storage Engine and Business.
Search¶
On the workspace list page, you can view basic information about all workspaces and search by workspace name keywords.
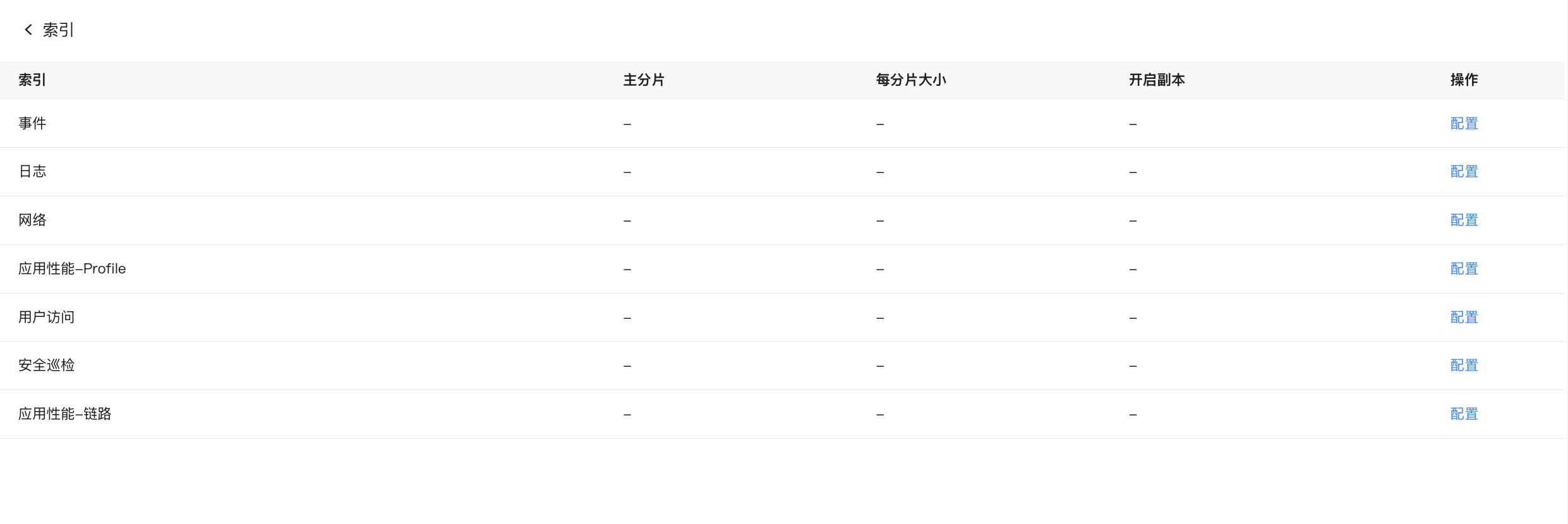
Index Configuration¶
Adjust the primary shard, shard size, and replica shard settings for all index templates in the current workspace.
Click the Configure button next to the data type to customize the "primary shard", "shard size", "hot data retention period", enable "replica", and adjust "advanced configurations".
Among them, under the Volcengine base, the storage policies for traces, logs, and custom log indices include:
- Standard storage: Configure hot data;
- Infrequent access storage: Configurable when standard storage duration is 7 days or more;
- Archive storage: Configurable when standard storage duration is 30 days or more.
Note
-
Enabling replicas creates a redundant copy of the index shards by default;
-
Enabling advanced configurations allows modification of the index mapping template, including parameters related to tokenization.
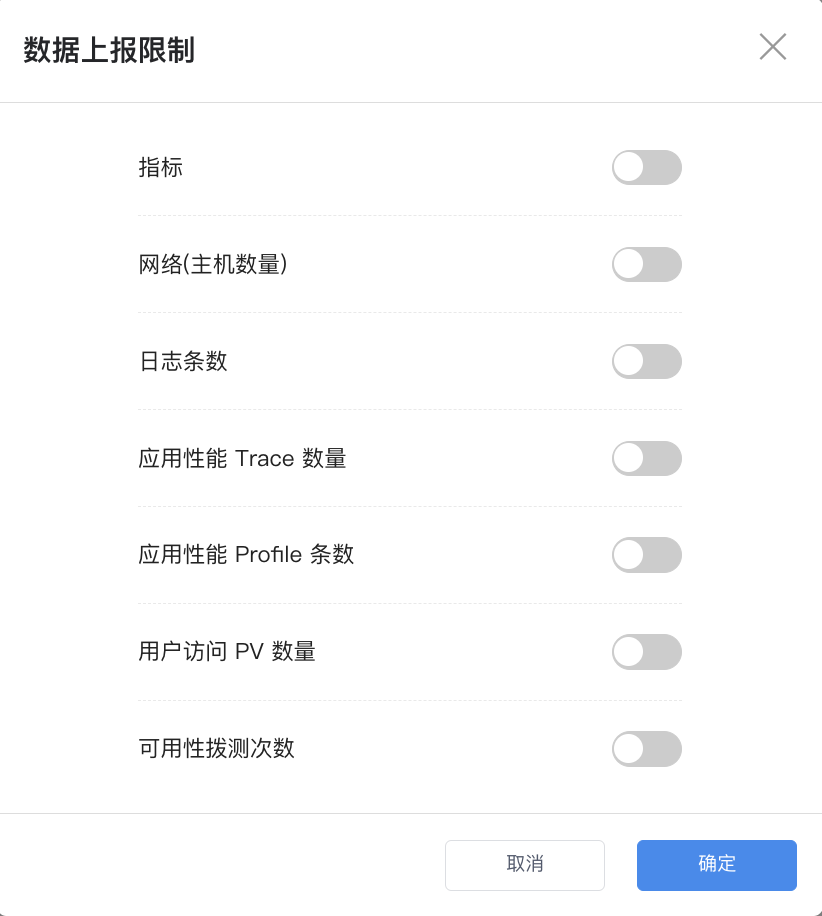
Data Reporting Limits¶
To meet the needs of users with the same role within a workspace, configure data reporting limits based on a "day" dimension to determine whether a specific type of data triggers a threshold. Once triggered, subsequent data reports will not be written to the database and will be discarded, thus saving resource usage costs.
As shown in the figure, you can configure limits for Metrics, NETWORK (host count), log entries, APM Trace counts, APM Profile counts, RUM PV counts, and Synthetic Testing frequencies.
Note
-
0means all corresponding data will be discarded without being written, with no upper limit; -
Since Metrics and NETWORK data are counted based on Time Series and NETWORK dimensions, there is no numerical limit; only enabling data write restrictions or unlimited modes apply.
View Members¶
Click to enter the corresponding workspace members page where you can view all member details of that workspace.
You can perform operations such as searching, modifying roles, and deleting.
Note
A workspace can only have one owner. Changing another member to the owner will demote the original owner to an administrator.
Add User¶
- Click to enter the add page;
- Select members;
- Set role permissions;
- Click confirm.
Note
You can only add existing system members here. If adding a new system member, they must first be added successfully on the User > Add User page before returning here to proceed.
Modify/Delete Member¶
Click to modify the workspace configuration or directly delete the workspace.
Tenant Configuration Management¶
Note
Only applicable to workspaces using the ScopeDB engine.
- Workgroup: The actual executing work group. After configuration, all queries in this workspace will be executed by the specified workgroup and will not enter the default workgroup within the cluster.
- Query concurrency limit: Default 50 queries. The number of concurrent queries allowed within the workspace; exceeding this limit requires queuing.
- Sampling threshold: Default 5 million. Automatically enables sampling queries and returns data when the queried data volume reaches the preset configuration.
- Asynchronous execution timeout: Default 2 minutes. Query timeout duration.
- Disable streaming aggregation: Default off.
Delete Workspace¶
After clicking to delete the workspace, users will no longer be able to log into that workspace, and data will stop being reported.
The system will not immediately clean up data and configurations but will retain them for seven days as a buffer to avoid unnecessary complications caused by accidental deletions.