RUM Metric Detection¶
RUM Metric Detection is used to monitor the metric data of user access within the workspace. By setting threshold ranges, alerts can be triggered when the metrics reach the threshold. It supports setting alerts for individual metrics and customizing alert levels.
Use Case¶
Support the monitoring of metric data including Web, Android, iOS and Miniapp application types. For example, you can monitor the JS error rate based on the city dimension on the web side.
Setup¶
Step 1: Detection Configuration¶
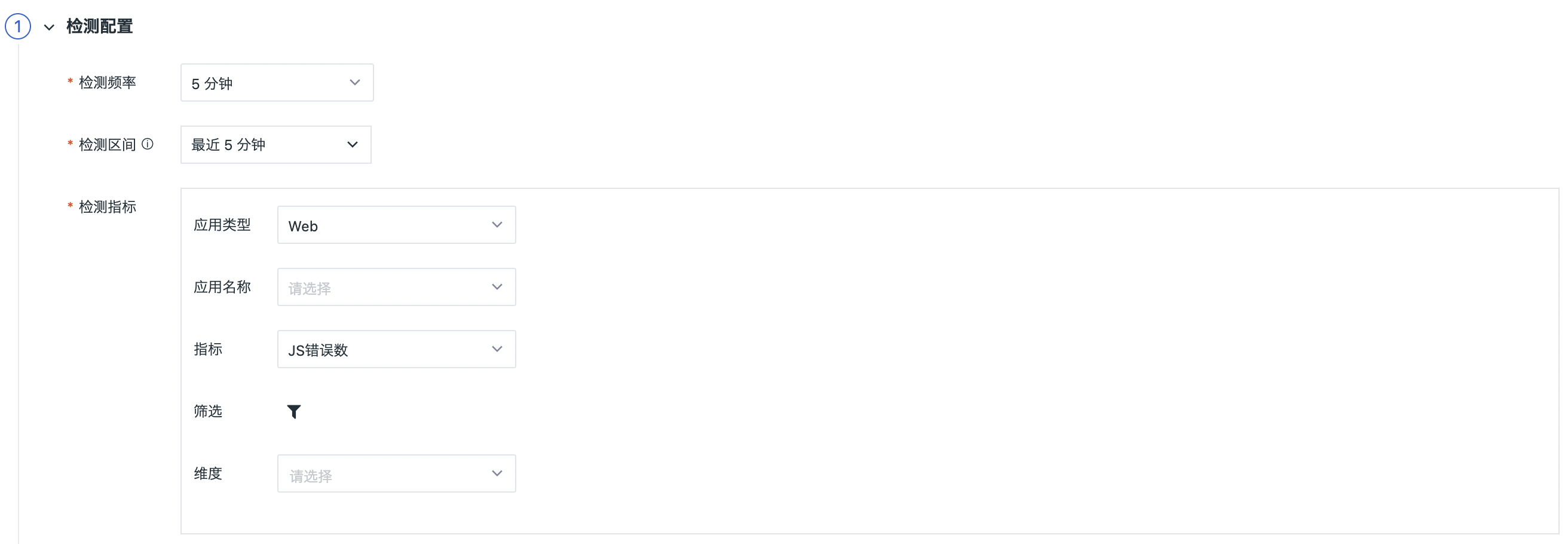
Detection Frequency: The execution frequency of detection rules, including 1m/5m/15/30m/1h/6h (5m is selected by default).
Detection Interval: The time range of detection index query when each task is executed. The optional detection interval will be different due to the influence of detection frequency.
| Detection Frequency | Detection Interval (Drop-down Option) |
|---|---|
| 1m | 1m/5m/15m/30m/1h/3h |
| 5m | 5m/15m/30m/1h/3h |
| 15m | 15m/30m/1h/3h/6h |
| 30m | 30m/1h/3h/6h |
| 1h | 1h/3h/6h/12h/24h |
| 6h | 6h/12h/24h |
Detection Metrics: Set the metric of detection data. Support to set the metric data of all/single applications within a certain time range under a single application type in the current workspace. For example, in the current workspace, all the metric data applied under the Web type.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Description | Types of applications supported by User Access Monitoring, including Web, Android, iOS, Miniapp. |
| Application Name | Obtain the corresponding application list based on the application type, and support all selection and single selection. |
| Metrics | A list of metrics obtained based on application types, Web/Miniapp((including JS Error Number, JS Error Rate, Resource Error Number, Resource Error Rate, Average First Render Time, Average Page Load Time, LCP (largest_contentful_paint), FID (first_input_delay), CLS (cumulative_layout_shift), FCP (first_contentful_paint), and so on. Android/IOS(including startup time, total crashes, total crashes, resource errors, resource errors, FPS, average page load time, and so on.) |
| Filtering | Based on the metric label, the data of detection metric is screened and the detection data range is limited. Support to add one or more label filters, and support fuzzy matching and fuzzy mismatching filters. |
| Detect Dimension | The corresponding string type (keyword) fields in the configuration data can be selected as detection dimensions. At present, the detection dimensions support selecting up to three fields. Through the combination of fields of multiple detection dimensions, a certain detection object can be determined, and the guance will judge whether the statistical index corresponding to a detection object meets the threshold of trigger conditions, and if it meets the conditions, an event will be generated. (For example, if the instrumentation dimensions host and host_ip are selected, the instrumentation object can be {host: host1, host_ip: 127.0.0.1}.) |
Web / Miniapp Metric Description
| Metric | Query Sample |
| Number of JS Errors | R::js_error:(count(`error_message`)) {`app_id` = '#{appid}'} |
| JS Error Rate | F::dataflux__dql:(exec_expr (expr='data1.count/data2.count*100', pre_func='SUM', data1 = dql("R::page:(count(`page_url`) as count) {`app_id` = '#{appid}',`page_js_error_count` > 0}"), data2 = dql("R::page:(count(`page_url`) as count) {`app_id` = '#{appid}'}") )) |
| Number of resource errors | R::resource:(count(`resource_url`)) {`app_id` = '#{appid}',( `resource_status_group` = '4xx' || `resource_status_group` = '5xx')} |
| Resource Error Rate | F::dataflux__dql:(exec_expr (expr='data1.count/data2.count*100', pre_func='SUM', data1 = dql("R::resource:(count(`page_url`) as count) {`app_id` = '#{appid}',`resource_status` >= 400}"), data2 = dql("R::resource:(count(`page_url`) as count) {`app_id` = '#{appid}'}") )) |
| Average First Rendering Time | R::page:(avg(page_fpt)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} |
| Average Page Loading Time | R::view:(avg(loading_time)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} |
| Number of Slow Page Loads | R::resource:(count(resource_load)){`app_id` = '#{appid}',`resource_load`>8000000000,resource_type='document'} |
| Average Resource Loading Time | R::resource:(avg(`resource_load`) as `加载耗时` ) {`app_id` = '#{appid}',resource_type!='document'} |
| LCP (largest_contentful_paint) | Includes aggregate functions: avg、P75、P90、P99 R::view:(avg(largest_contentful_paint)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`largest_contentful_paint`,75)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`largest_contentful_paint`,90)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`largest_contentful_paint`,99)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} |
| FID (first_input_delay) | Includes aggregate functions: avg、P75、P90、P99 R::view:(avg(first_input_delay)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`first_input_delay`,75)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`first_input_delay`,90)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`first_input_delay`,99)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} |
| CLS (cumulative_layout_shift) | Includes aggregate functions: : avg、P75、P90、P99 R::view:(avg(cumulative_layout_shift)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`cumulative_layout_shift`,75)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`cumulative_layout_shift`,90)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`cumulative_layout_shift`,99)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} |
| FCP (first_contentful_paint) | Includes aggregate functions: : avg、P75、P90、P99 R::view:(avg(first_contentful_paint)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`first_contentful_paint`,75)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`first_contentful_paint`,90)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} R::view:(percentile(`first_contentful_paint`,99)){`app_id` = '#{appid}'} |
Android / IOS Metric Description
| Metric | Query Sample |
| Startup Time Consuming | |
| Total Number of Crashes | |
| Total Collapse Rate | |
| Number of Resource Errors | |
| Resource Error Rate | |
| FPS | |
| Average Page Loading Time | |
| Average Resource Loading Time | |
| Caton Number |
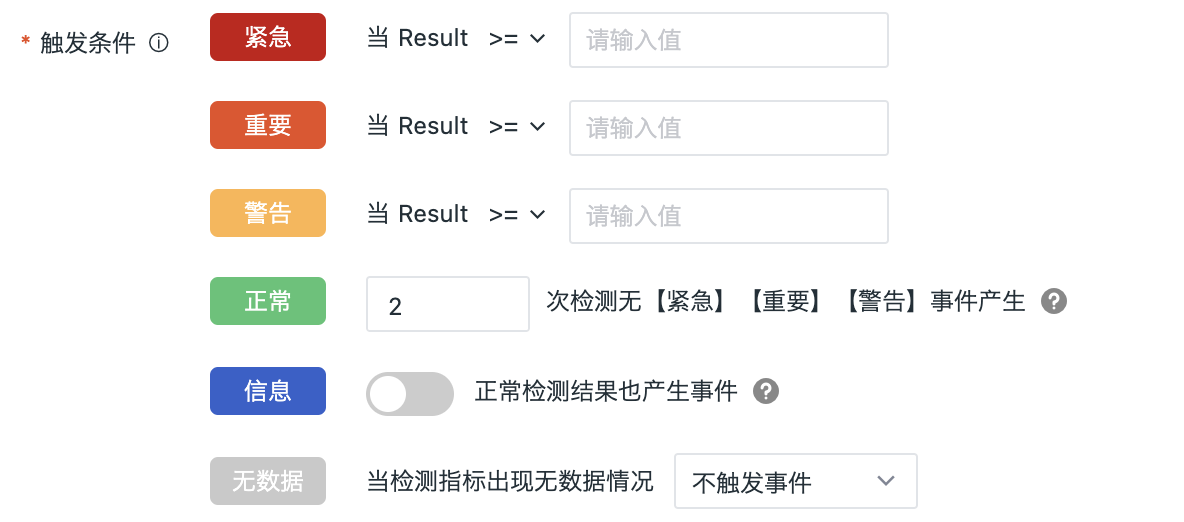
Trigger Condition: Set the trigger condition of alert level; You can configure any of the following trigger conditions: Critical, Error, Warning, No Data, or Information.
Configure the trigger condition and severity. When the query result is multiple values, an event will be generated if any value meets the trigger condition.
See Event Levels.
I. Alert levels: Critical (red), Important (orange), Warning (yellow): Based on the configured conditions using operators.
II. Alert levels: OK (green), Information (blue): Based on the configured number of detections, as explained below:
- One test is performed for each test task, if "test frequency = 5 minutes", then one test = 5 minutes
- You can customize the number of tests, such as "Test frequency = 5 minutes", then 3 tests = 15 minutes
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| OK | After the detection rule takes effect, if the result of an urgent, important, or warning abnormal event returns to normal within the configured number of custom detections, a recovery alert event is generated.  Recovery alert events are not affected by Mute Alerting. If no detection count is set for recovery alert events, the alert event will not recover and will always appear in the Events > Unrecovered Events List. Recovery alert events are not affected by Mute Alerting. If no detection count is set for recovery alert events, the alert event will not recover and will always appear in the Events > Unrecovered Events List. |
| Information | Events are generated even for normal detection results. |
III. Alert level: No Data (gray): The no data state supports three configuration strategies: Trigger No-Data Event, Trigger Recovery Event, and Untrigger Event.
Step 2: Event Notification¶
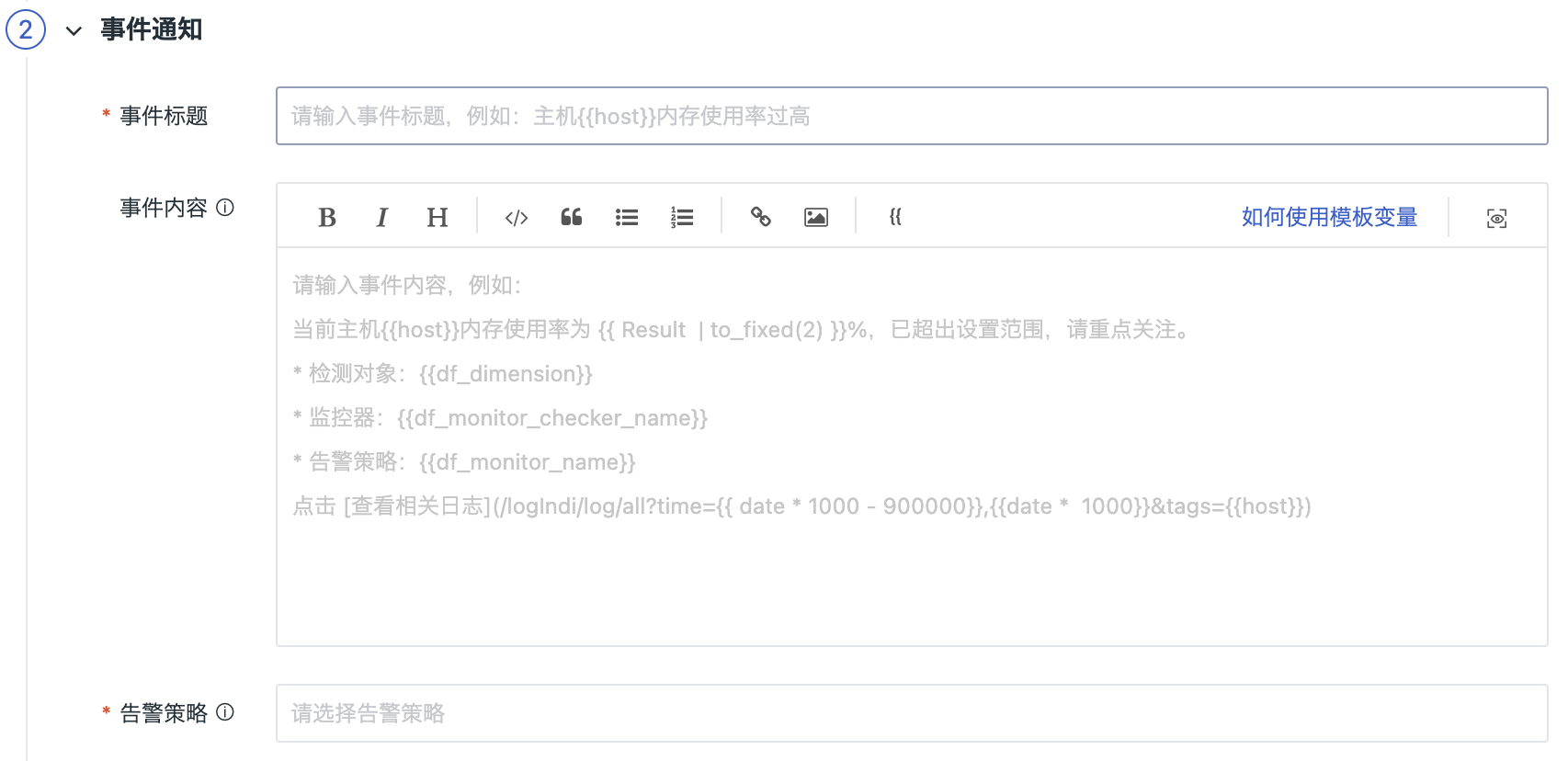
Event Title: Set the event name of the alert trigger condition; support the use of preset template variables.
Event Content: The content of the event notification sent when the trigger conditions are met. Support inputting text in Markdown format, previewing effects, the use of preset associated links and the use of preset template variables.
Note:
-
In the latest version, the Monitor Name will be automatically generated based on the Event Title input. In older monitors, there may be inconsistencies between the Monitor Name and the Event Title. To enjoy a better user experience, please synchronize to the latest version as soon as possible. One-click replacement with event title is supported.
-
Different alert notification targets support different Markdown syntax. For example, WeCom does not support unordered lists.
No Data Notification Configuration: Support customizing the content of the no data notification. If not configured, the official default notification template will be automatically used.
Alarm Strategy: After the monitoring meets the trigger conditions, immediately send an alert message to the specified notification targets. The Alert Strategy includes the event level that needs to be notified, the notification targets and the mute alerting period.
Step 3: Association¶
Associate Dashboard: Every monitor supports associating with a dashboard for quick navigation and viewing.
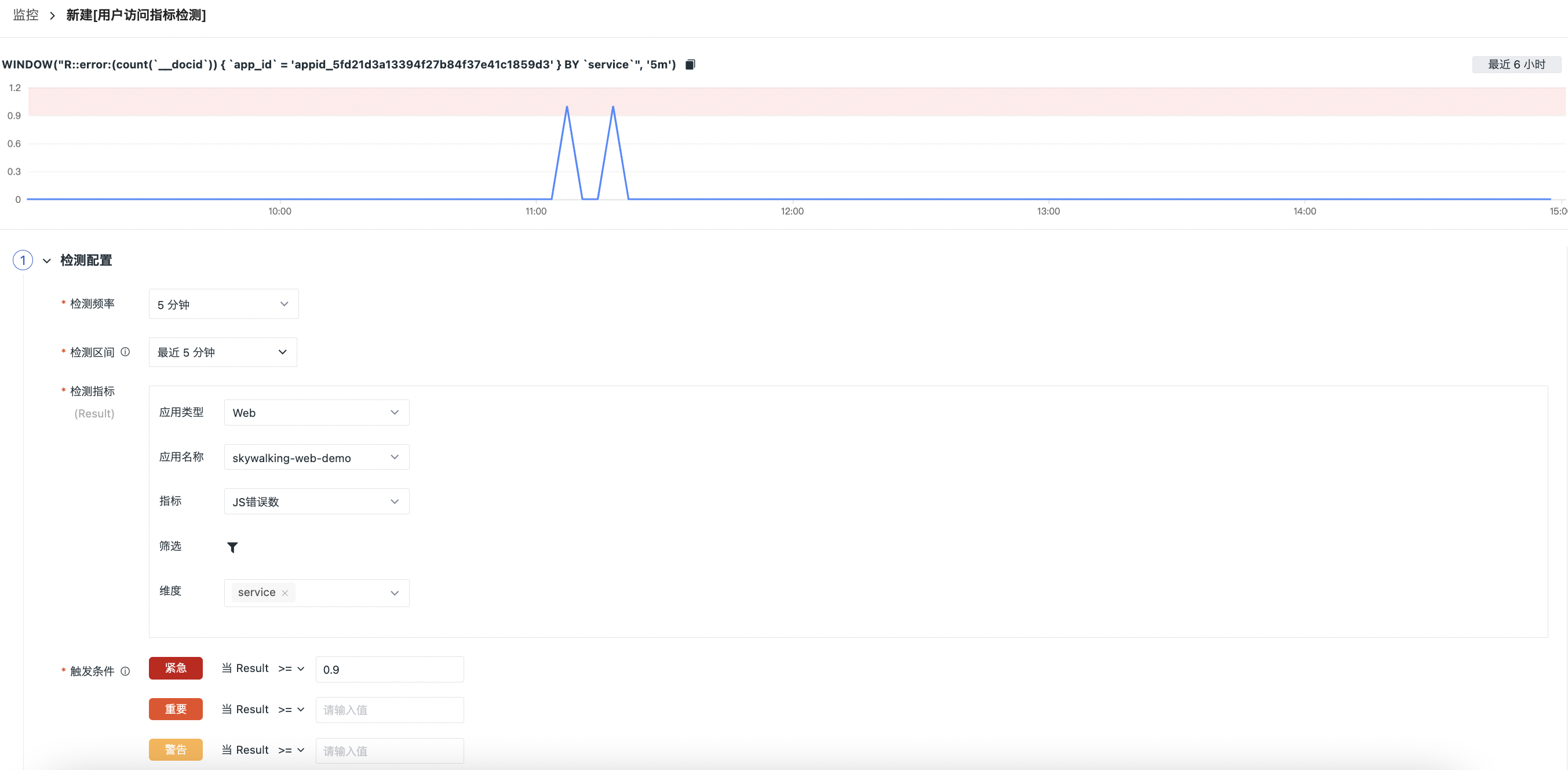
Example¶
Monitor the number of JS errors on the web side of skywalking-web-demo based on the service dimension.