Detection Rules¶
The system supports various monitoring detection rules, covering different data ranges.
Rule Types¶
Rule Name |
Data Range |
Basic Description |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold Detection | All | Abnormal detection of metric data based on set thresholds. |
| Mutation Detection | Metrics(M) | Abnormal detection of sudden abnormal behavior in metrics based on historical data, suitable for business data and short time windows. |
| Interval Detection | Metrics(M) | Detection of abnormal data points in metrics based on dynamic threshold ranges, suitable for stable trend timelines. |
| Interval Detection V2 | Metrics(M) | Detection of abnormal data points in metrics based on dynamic threshold ranges, suitable for stable trend timelines. |
| Outlier Detection | Metrics(M) | Detects whether there is an outlier deviation in the metrics/statistics of the detection object under a specific group. |
| Log Detection | Logs(L) | Abnormal detection of business applications based on log data. |
| Process Anomaly Detection | Process Objects(O::host_processes) |
Periodically detects process data to understand process anomalies. |
| Infrastructure Survival Detection V2 | Objects(O) | Sets survival conditions based on infrastructure object data to monitor the stability of infrastructure. |
| Application Performance Metric Detection | Traces(T) | Sets threshold rules based on application performance monitoring data to detect abnormal situations. |
| User Access Metric Detection | User Access Data(R) | Sets threshold rules based on user access monitoring data to detect abnormal situations. |
| Composite Detection | All | Combines multiple monitors' results into one monitor through expressions, and triggers alarms based on the combined results. |
| Security Check Anomaly Detection | Security Checks(S) | Abnormal detection based on data generated by security checks, which can effectively perceive the health status of hosts. |
| Synthetic Testing Anomaly Detection | Synthetic Testing Data(L::Type) |
Sets threshold rules based on synthetic testing data to detect abnormal situations. |
| Network Data Detection | NETWORK(N) | Sets threshold rules based on network data to detect the stability of network performance. |
| External Event Detection | Others | Sends abnormal events or records generated by third-party systems via POST requests to an HTTP server after specifying a URL address, generating event data. |
| Infrastructure Change Detection | Objects(O) | Monitors various change behaviors based on tracking the lifecycle of infrastructure, accurately identifying configuration drifts and illegal operations. |
General Configuration¶
Detection Configuration¶
Set corresponding detection frequencies, detection intervals, and detection metrics for different detection rules.
Event Notifications¶
Event Title¶
Defines the event name that triggers alarm conditions; you can use predefined template variables.
Note
In the latest version, the monitor name will be automatically generated after entering the event title. There may be inconsistencies between the monitor name and the event title in older monitors, so it is recommended to synchronize to the latest version.
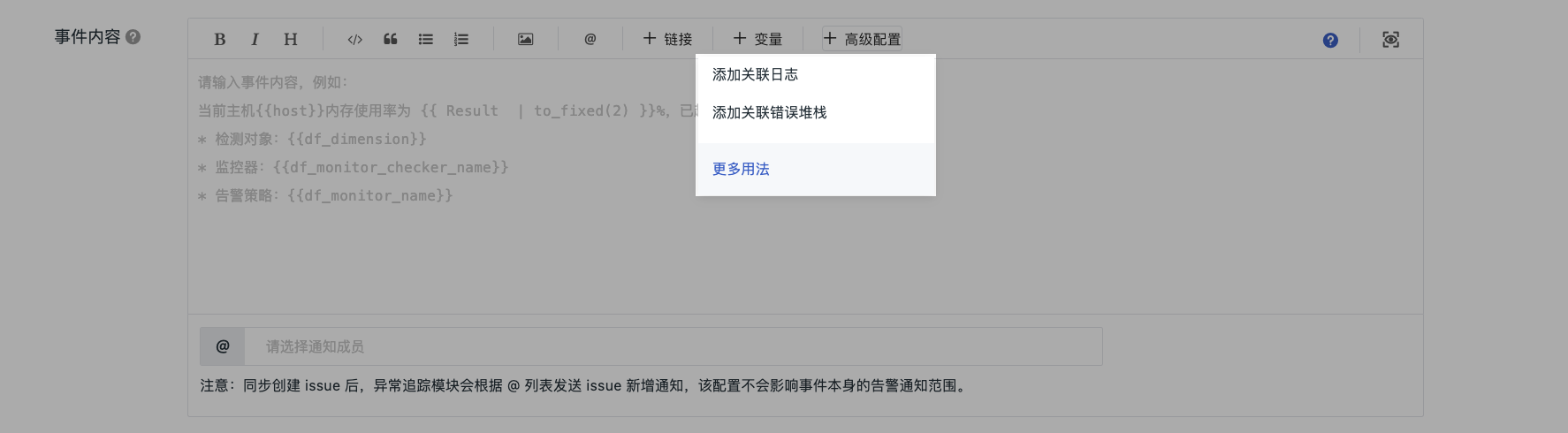
Event Content¶
Write the content of the event notification. When the trigger conditions are met, the system will send this content externally. It generally includes the following information:
- Main body in Markdown format;
- Can insert associated links and template variables;
- Add associated logs or error messages based on advanced settings;
- Target notification members for sending event content.
Note
The @ member configuration will only take effect and send the event content to the specified member when correlation with anomaly tracking is enabled.
Associated Links¶
Monitors will automatically generate jump links based on the detection metrics in the detection configuration. You can adjust filter conditions and time ranges after inserting links. Generally, it is a fixed link prefix containing the current domain name and workspace ID; you can also choose to customize the jump links.
Among these, if you need to insert a link to jump to the dashboard, based on the above logic, you will also need to supplement the dashboard's ID and name, adjusting view variables and time ranges as needed.
Custom Advanced Settings¶
Through advanced settings, you can add associated logs or error stacks in the event content to view context data when anomalies occur.
- Adding associated logs:
Query:
For example: Get a log message with an index of default:
Associated log:
- Adding associated error stack
Query:
{% set dql_data = DQL("T::re(`.*`):(`error_message`,`error_stack`){ (`source` NOT IN ['service_map', 'tracing_stat', 'service_list_1m', 'service_list_1d', 'service_list_1h', 'profile']) AND (`error_stack` = exist()) } LIMIT 1") %}
Associated error stack:
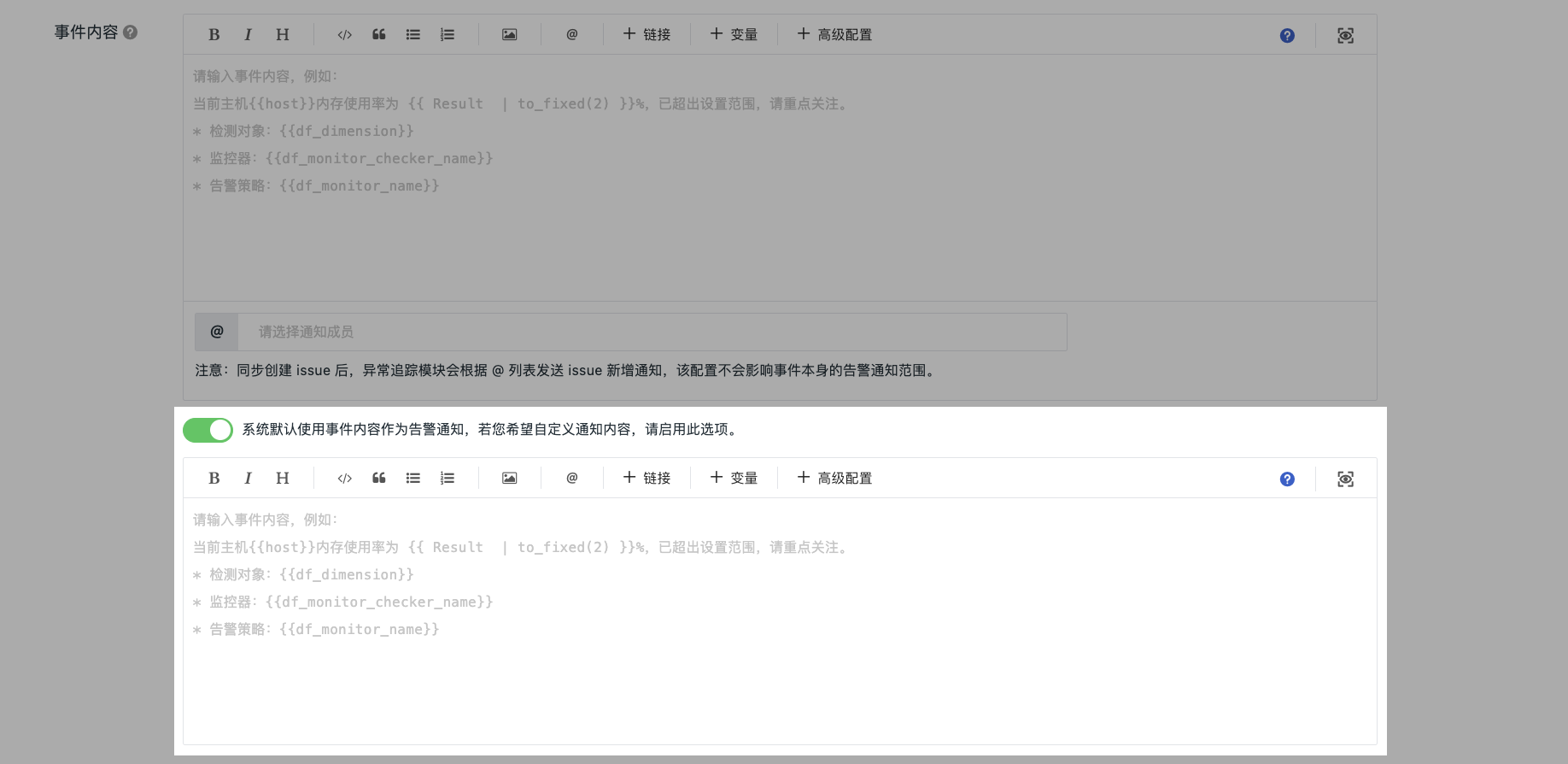
Custom Notification Content¶
By default, the system will use the event content as the alarm notification content. If you need to customize the actual external notification, you can enable the switch here and enter the notification information.
Note
Different alarm notification targets support different Markdown syntax. For example, WeCom does not support unordered lists.
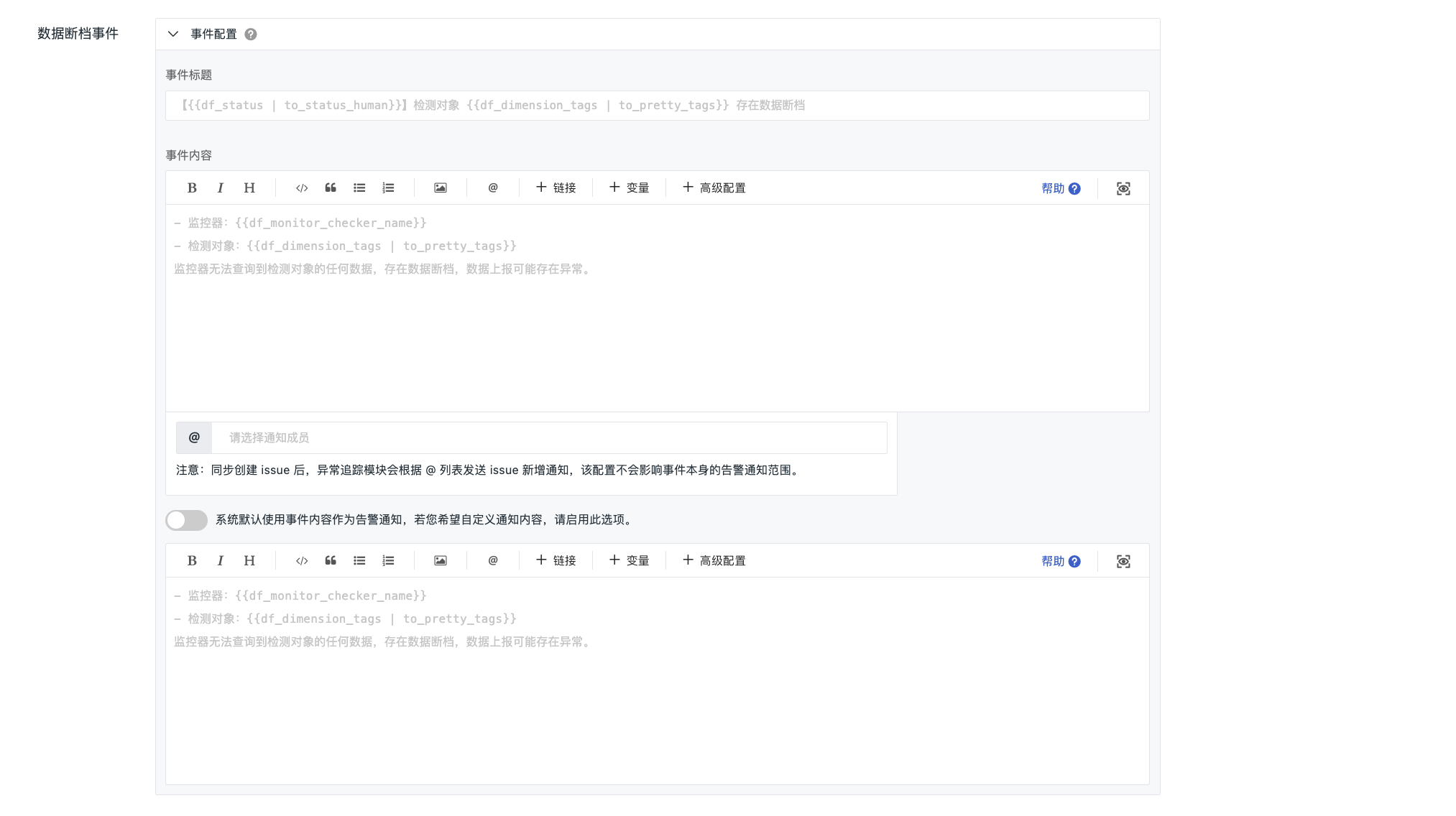
Data Gap Events¶
Customize the content of data gap notifications. You can configure the title and content of such events when they are sent externally.
If this is not configured, the official default notification template will be used automatically when sending externally.
Correlation with Incident Tracking¶
After enabling the correlation, if an anomaly event occurs under this monitor, an Issue will be created synchronously. You can choose to create an Issue for different event levels.
- Select the event level;
- Define the final level of the generated Issue;
- Select the responsible person for this type of Issue;
- Choose the delivery channel;
- Optionally select whether to close the Issue synchronously after the event is recovered.
Issues generated here can be viewed in Incident > Channel you have selected.
Alert Configuration¶
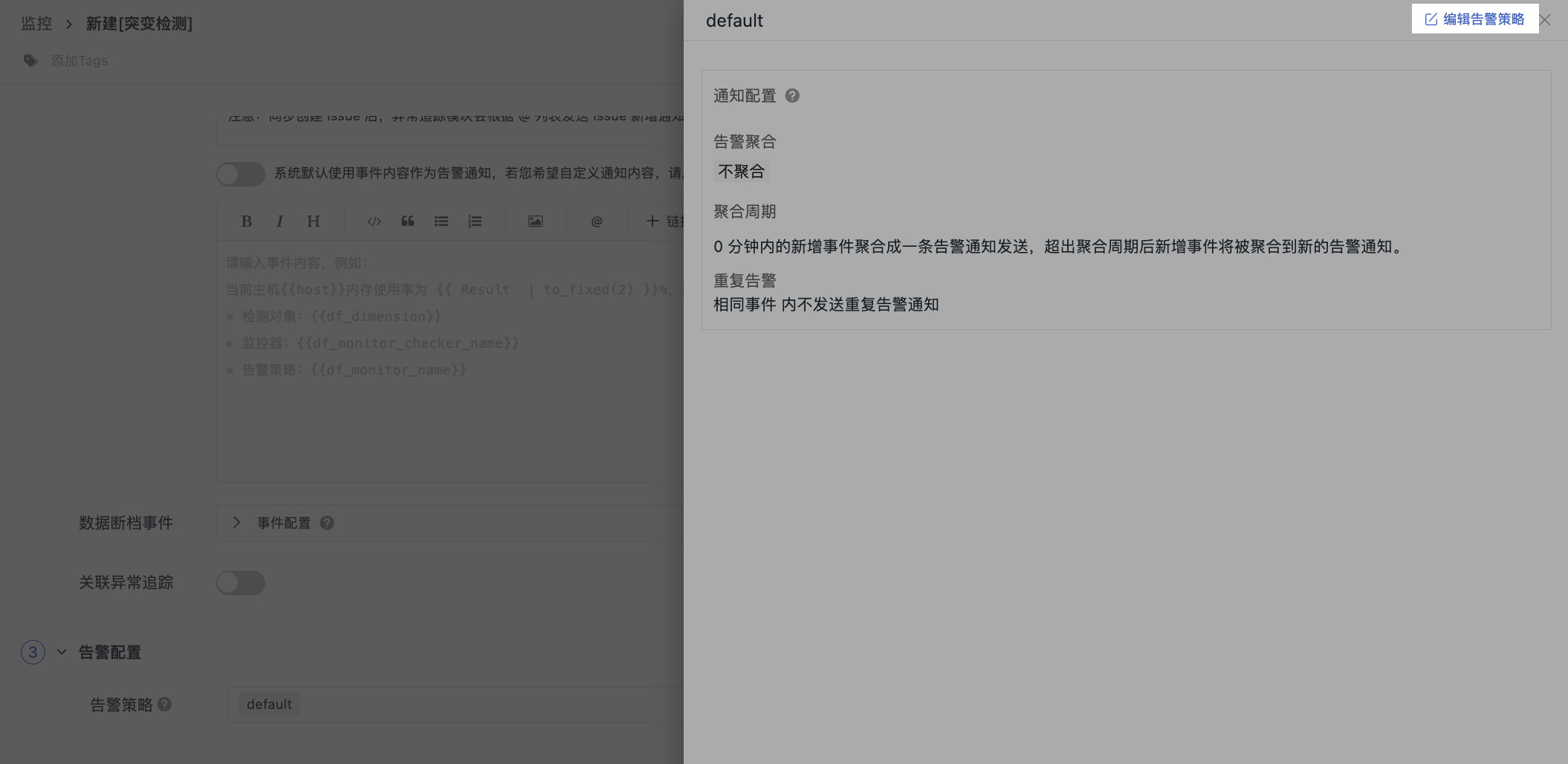
After meeting the trigger conditions, immediately send an alert message to the specified notification target. The alert strategy includes the event levels to notify, notification targets, and alert mute cycles.
Alert strategies support single or multiple selections. Clicking the strategy name expands the detail page. To modify the strategy, click Edit Alert Strategy.
Association¶
Supports associating monitors with dashboards for quick jumps and visualizing related data.
Permissions¶
After setting operation permissions for the monitor, ensure that different users perform actions according to their roles and permission levels.
- Not enabling this configuration: Follow the default permissions for "Monitor Configuration Management";
- Enabling this configuration and selecting custom permission objects: Only the creator and authorized objects can enable/disable, edit, or delete the rules set for this monitor;
- Enabling this configuration without selecting custom permission objects: Only the creator has the enable/disable, edit, and delete permissions for this monitor.
Note
The Owner role in the current workspace is not affected by the operation permission configuration here.
Recover Monitor¶
You can view the status, last update time, creation time, and creator of existing monitors. You can recover a monitor to view its historical configuration, helping you quickly communicate and collaborate with other team members to update the monitor.
Operation Example:
In Monitoring > Monitors, select an existing monitor to edit. On the monitor configuration page, click the button in the top-right corner to view the monitor's status, last update time, creation time, and creator.
Click the button to the right of the update time in the above image to open a new browser window showing the previous version of the monitor configuration;
Click Restore This Version in the top-right corner of the previous version of the monitor. Confirm the restoration in the pop-up dialog box to restore the monitor configuration to the previous version for editing and saving.